Discover practical strategies and expert advice on how to effectively manage your personal finances in our comprehensive guide to financial success.
Creating a Budget

Creating a budget is the cornerstone of effective personal finance management. It allows you to track your income and expenses, ensuring you’re spending less than you earn and working towards your financial goals. Here’s a step-by-step guide to building a successful budget:
1. Track Your Income and Expenses
Start by recording all sources of income. This could include your salary, wages, bonuses, investment returns, or any other regular income streams. Next, track all your expenses diligently. Utilize banking apps, spreadsheets, or budgeting apps to categorize and monitor your spending habits.
2. Categorize Your Spending
Divide your expenses into fixed and variable categories. Fixed expenses are consistent each month, such as rent/mortgage, loan payments, and utilities. Variable expenses fluctuate, including groceries, dining out, entertainment, and shopping.
3. Set Realistic Financial Goals
Define short-term and long-term financial goals. Whether it’s saving for a down payment, paying off debt, or investing, having specific goals gives your budget direction and motivates you to stick to it.
4. Determine Your Spending Limits
Based on your income, expenses, and goals, set realistic spending limits for each category. Look for areas where you can potentially cut back without drastically impacting your lifestyle. The 50/30/20 budget is a popular guideline, allocating 50% of your income to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings and debt repayment.
5. Review and Adjust Regularly
A budget is not static. Review it regularly, preferably monthly, to assess your progress, identify areas needing adjustment, and ensure it aligns with your evolving financial situation and goals.
Tracking Your Expenses
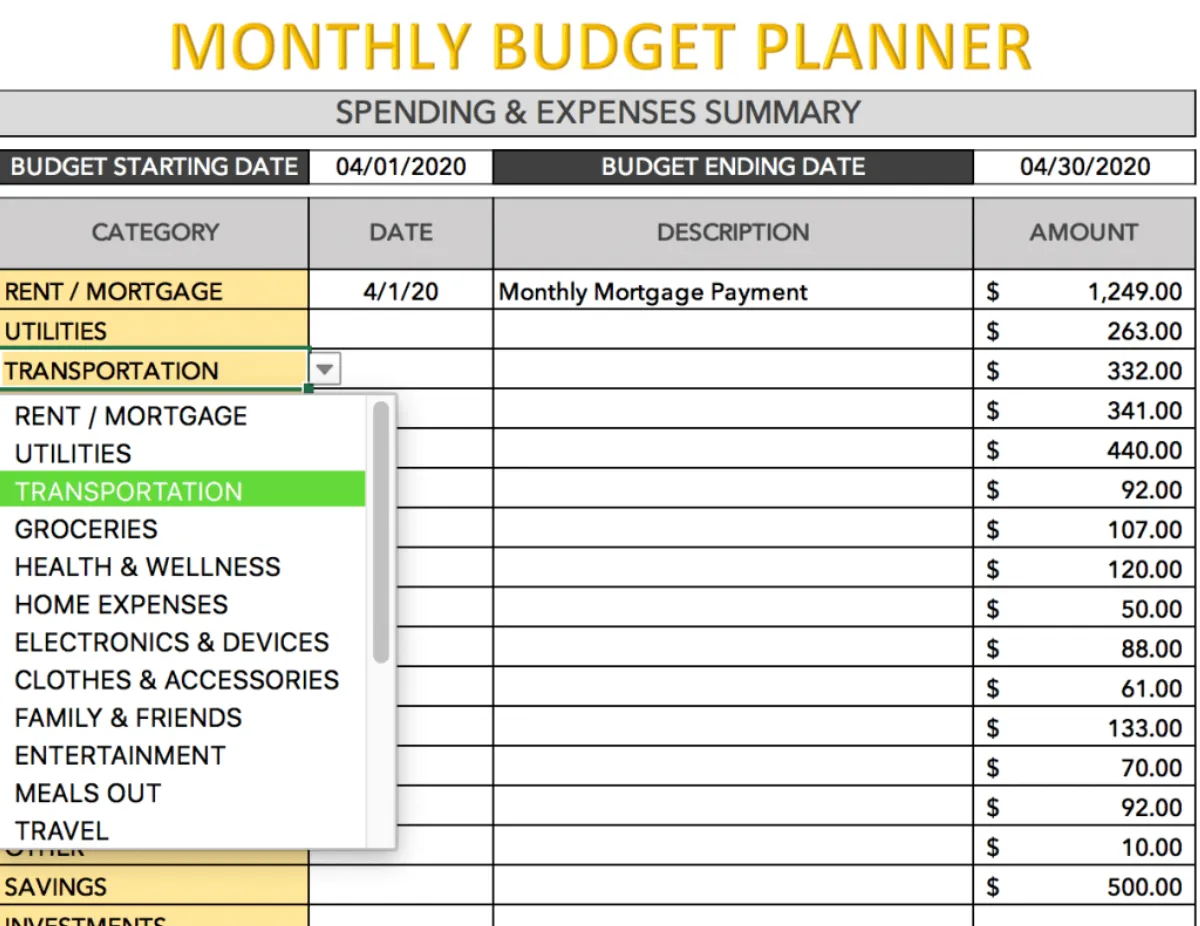
One of the most crucial aspects of effective personal finance management is understanding where your money goes. Tracking your expenses provides valuable insights into your spending habits, allowing you to identify areas where you can cut back and save more effectively.
There are various methods for tracking expenses, each with its own advantages:
1. Spreadsheet or Budgeting Apps
Utilizing spreadsheets or dedicated budgeting apps are popular and efficient ways to track expenses. These tools enable you to categorize your spending, set budgets, and monitor your progress over time. Many apps offer features like bank synchronization, automated categorization, and personalized financial reports.
2. Envelope System
This traditional method involves allocating cash to different envelopes designated for specific expense categories. By physically separating your money, you visually track your spending and limit yourself to the cash available in each envelope.
3. Bank Statements and Receipts
While less technologically advanced, reviewing your bank statements and keeping receipts allows for manual tracking. You can categorize your spending by highlighting or making notes on your statements, providing a historical record of your expenses.
Regardless of the chosen method, consistency is key. Aim to track your expenses regularly, whether daily, weekly, or monthly. This consistent practice helps you stay aware of your spending patterns and identify potential areas for improvement.
Setting Financial Goals
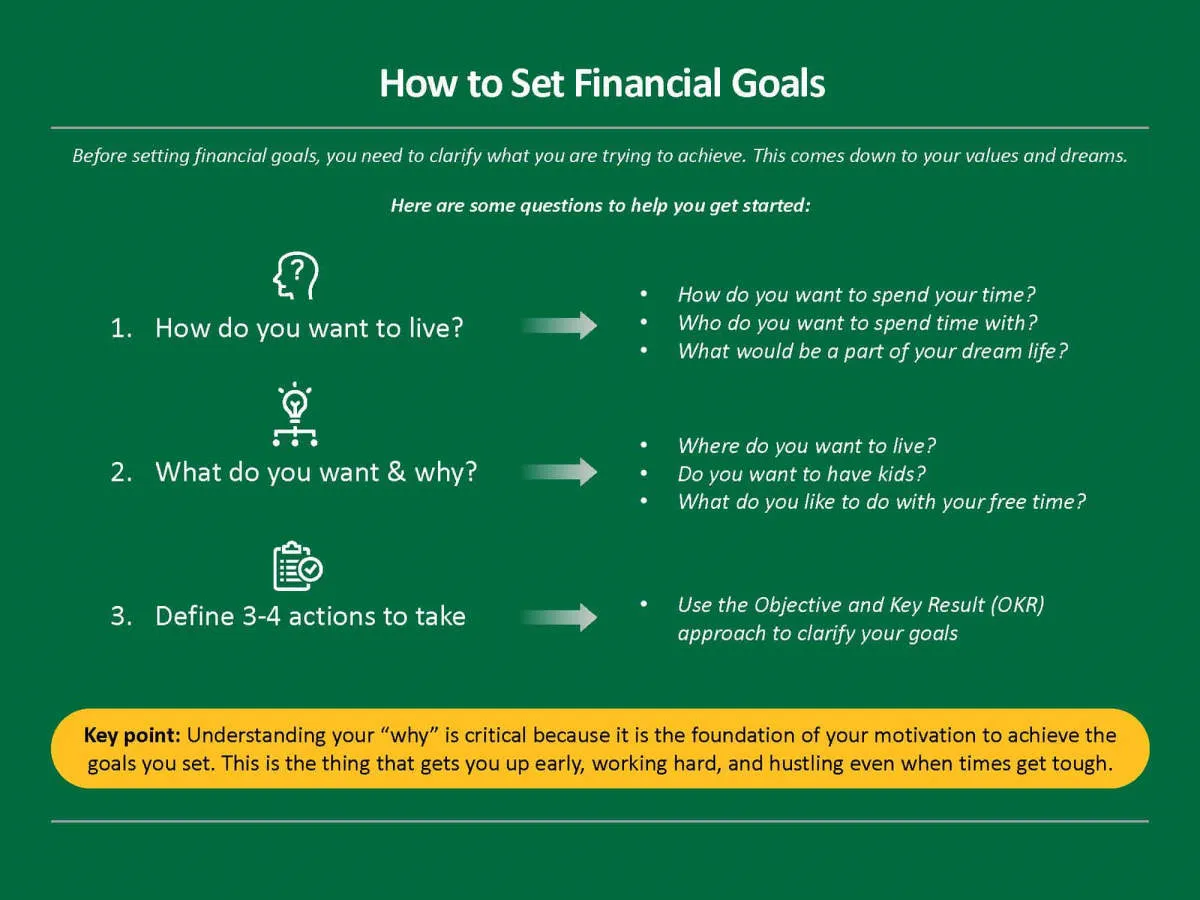
Effective personal finance management hinges on well-defined financial goals. Without clear objectives, it’s easy to overspend, under-save, and lose track of your financial progress. Here’s how to set the right goals for your financial journey:
1. Identify Your Goals:
What do you want to achieve with your money? Consider both short-term and long-term aspirations. Examples include:
- Short-term: Building an emergency fund, paying off credit card debt, saving for a down payment on a car or home, taking a vacation.
- Long-term: Saving for retirement, purchasing a house, funding your children’s education, starting a business.
2. Make Your Goals SMART:
Ensure your goals are:
- Specific: Clearly define what you want to achieve (e.g., “Save $5,000 for a down payment” instead of “Save for a house”).
- Measurable: Quantify your goals with specific numbers (e.g., “Save $100 per week”).
- Achievable: Set realistic goals you can reasonably accomplish with your income and expenses.
- Relevant: Align your goals with your values and priorities.
- Time-bound: Give yourself deadlines to stay motivated (e.g., “Save $5,000 for a down payment within two years”).
3. Prioritize Your Goals:
You may have multiple goals, so prioritize them based on their importance to you. This helps you focus your efforts and resources on the most critical objectives first.
4. Break Down Large Goals:
Large goals can feel overwhelming. Divide them into smaller, manageable steps to make them less daunting and track progress more effectively.
5. Write Down Your Goals:
Putting your goals in writing makes them more tangible and increases your commitment to achieving them. Review your goals regularly to stay on track.
Building an Emergency Fund

One of the most crucial aspects of managing personal finances efficiently is establishing a robust emergency fund. This fund serves as a financial safety net, providing peace of mind and a buffer against unexpected expenses or financial hardships.
Why is an Emergency Fund Important?
Life is unpredictable, and unexpected events like medical emergencies, job loss, or car repairs can derail even the most carefully crafted budget. An emergency fund acts as a financial cushion, allowing you to navigate these situations without incurring debt or depleting your savings.
How Much Should You Save?
A general guideline is to aim for 3-6 months’ worth of living expenses in your emergency fund. This ensures you can cover essential costs like rent/mortgage payments, utilities, groceries, and transportation for an extended period.
Where to Keep Your Emergency Fund
Accessibility and safety are key considerations when choosing where to keep your emergency fund. A high-yield savings account at a reputable bank or credit union offers a balance of liquidity and growth, allowing you to access your funds quickly while earning interest.
Tips for Building Your Emergency Fund
- Start small and be consistent: Even small contributions add up over time. Set a realistic savings goal and automate regular transfers to your emergency fund.
- Cut expenses and redirect funds: Identify areas where you can reduce spending and redirect those funds towards your emergency savings.
- Treat your emergency fund as non-negotiable: Avoid dipping into your emergency fund for non-essential expenses. Its purpose is to provide financial security during unforeseen circumstances.
- Replenish your fund after use: If you need to tap into your emergency fund, prioritize replenishing it as soon as possible to maintain your financial safety net.
Investing Wisely

Investing is a crucial aspect of building long-term wealth and achieving your financial goals. However, it’s important to approach investing strategically and make informed decisions.
Define Your Financial Goals:
Before investing, identify your short-term and long-term financial goals. Are you saving for retirement, a down payment on a house, or your child’s education? Clearly defined goals will help shape your investment strategy.
Determine Your Risk Tolerance:
Investing always involves some level of risk. Your risk tolerance refers to your ability to withstand fluctuations in the value of your investments. Consider factors like your age, time horizon, and financial situation when determining your risk appetite.
Diversify Your Portfolio:
Diversification is key to mitigating risk. Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Spread your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. Diversifying within asset classes is also essential. For example, within stocks, invest in different sectors and industries.
Start Early and Be Patient:
The power of compounding is significant in investing. The earlier you start, the more time your investments have to grow. Be patient and avoid making impulsive decisions based on market fluctuations.
Research and Seek Professional Advice:
Thoroughly research any investment before committing your money. Consider factors like the company’s financials, industry trends, and management team. If needed, consult with a qualified financial advisor who can provide personalized guidance.
Reducing Debt

Debt can be a major source of stress and financial instability. Getting a handle on your debt is crucial for effective personal finance management. Here’s how:
1. Create a Debt Management Plan
Start by listing out all your debts, including the creditor, total amount owed, interest rate, and minimum monthly payment. This will give you a clear picture of what you’re dealing with.
2. Prioritize Your Debts
Not all debt is created equal. Focus on high-interest debts first, like credit cards, as they accrue more debt over time. Consider strategies like the debt snowball method (paying off the smallest debts first for motivation) or the debt avalanche method (tackling high-interest debts first to save money on interest).
3. Negotiate with Creditors
Don’t be afraid to reach out to your creditors and explain your financial situation. They may be willing to work with you by lowering your interest rate, waiving fees, or setting up a payment plan.
4. Explore Debt Consolidation Options
If you have multiple debts with high interest rates, consolidating them into one loan with a lower interest rate could simplify your payments and save you money.
5. Avoid Taking on New Debt
While you’re working on paying off existing debt, try to avoid taking on new debt unless absolutely necessary. Put off large purchases if possible and focus on living within your means.
6. Seek Professional Help
If you’re struggling to manage your debt on your own, don’t hesitate to seek help from a financial advisor. They can provide personalized guidance and support to help you get back on track.
Using Financial Tools

In today’s digital age, a plethora of financial tools can empower you to manage your money efficiently. These tools go beyond basic budgeting and can significantly simplify your financial life and help you reach your goals faster. Here are some key tools to consider:
Budgeting Apps and Software
These tools have revolutionized personal finance management. Apps like Mint, YNAB (You Need a Budget), and Personal allow you to:
- Track income and expenses automatically.
- Categorize spending to identify areas for improvement.
- Set and monitor budgets across various categories.
- Receive personalized insights and recommendations.
Investment Platforms
Whether you’re a beginner or experienced investor, platforms like Robinhood, Vanguard, and Fidelity offer:
- Access to various investment options (stocks, bonds, mutual funds, etc.).
- Tools for research and portfolio analysis.
- Automated investing features for hands-off management.
- Educational resources to make informed decisions.
Expense Tracking Tools
While budgeting apps often include expense tracking, dedicated apps like Expensify and Zoho Expense are particularly useful for:
- Scanning and logging receipts digitally.
- Creating expense reports for business or reimbursement.
- Tracking mileage and other business-related expenses.
Credit Monitoring Services
Protecting your credit score is crucial. Services like Credit Karma, Experian, and Equifax provide:
- Regular credit report updates from all three bureaus.
- Monitoring for potential identity theft and fraud.
- Insights into factors affecting your credit score.
- Tools and tips for credit improvement.
By taking advantage of these financial tools, you can gain a clearer picture of your finances, automate key tasks, and make more informed decisions to achieve your financial goals.
Reviewing Your Finances Regularly

Regular financial reviews are crucial for maintaining control over your money and achieving your financial goals. It’s not enough to create a budget or investment plan and then forget about it. Life is constantly changing, and your finances need to adapt accordingly.
How often should you review your finances? It depends on your individual circumstances and preferences. Some people find it helpful to do a quick check-in monthly, while others prefer a more comprehensive review quarterly or annually. The key is to find a frequency that works for you and stick to it.
What should you review? During your financial review, consider the following:
- Income and expenses: Are you earning more or less than you were previously? Have your expenses increased or decreased? Track your spending and see where your money is going.
- Budget: Is your current budget still realistic and aligned with your goals? Adjust it as needed to reflect changes in your income, expenses, or priorities.
- Debt: Are you making progress on paying down debt? Explore strategies to reduce debt faster, such as debt snowball or avalanche methods.
- Savings: Are you saving enough for your emergency fund, retirement, or other financial goals? If not, look for opportunities to increase your savings rate.
- Investments: Review your investment portfolio’s performance and risk tolerance. Rebalance your portfolio or adjust your investment strategy if necessary.
- Insurance coverage: Assess whether your current insurance policies (health, life, auto, etc.) still meet your needs and provide adequate coverage.
By reviewing your finances regularly and making adjustments as needed, you can stay on track financially and work towards achieving your goals. Remember, personal finance is an ongoing process, and regular check-ins are essential for success.
Understanding Financial Terms
Managing your finances effectively starts with a solid understanding of basic financial terms. Don’t let unfamiliar jargon intimidate you. Here are some key terms to grasp:
Income and Expenses
Income refers to the money you earn, such as your salary, wages, or investment returns. Expenses are the costs you incur, including rent, groceries, utilities, and entertainment.
Budgeting and Saving
A budget is a plan for how you will spend and save your money. Saving involves setting aside a portion of your income for future use, such as an emergency fund or retirement.
Debt and Credit
Debt is money you owe to another party. Common types include credit card debt, student loans, and mortgages. Credit refers to your ability to borrow money. A good credit score can make it easier to get loans with favorable terms.
Investing
Investing involves putting money into assets like stocks, bonds, or real estate with the goal of growing your wealth over time. Different investments carry varying levels of risk and potential return.
Seeking Professional Advice

While there are many resources available to help you manage your finances independently, sometimes seeking professional advice can be incredibly beneficial. Financial advisors can provide personalized guidance tailored to your specific financial situation, goals, and risk tolerance.
Here are some situations where seeking professional advice can be particularly helpful:
- You’re overwhelmed by debt and need help creating a plan for repayment.
- You’re unsure how to best invest your savings to reach your long-term financial goals.
- You’re planning for a major life event, such as buying a home, starting a family, or retiring.
- You need help navigating complex financial products or strategies.
When choosing a financial advisor, consider the following:
- Their certifications and experience
- Their fee structure
- Whether they are a fiduciary, meaning they are legally obligated to act in your best interests
- Their communication style and whether it aligns with your needs
Remember, a financial advisor can provide valuable insights and support, but ultimately, you are responsible for making decisions about your finances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective personal finance management involves budgeting, saving consistently, investing wisely, and controlling spending habits. By following these tips, individuals can secure their financial future and achieve their goals.

