Financial literacy is crucial for teenagers to develop responsible money management skills, understand the value of savings, and make informed financial decisions for a secure future.
Understanding Money Management

Understanding money management is crucial for teenagers as it sets the foundation for a healthy financial future. It’s about more than just spending less than you earn; it’s about making informed decisions about your finances and developing positive habits that will benefit you throughout your life. Here are some key aspects of money management teenagers should learn:
Budgeting
Creating a budget is essential for understanding where your money goes. Track your income and expenses to see how much you have coming in and where you’re spending it. This can help you identify areas where you can cut back and save more effectively.
Saving
Developing a habit of saving is crucial for future financial security. Start by setting realistic savings goals, whether it’s for a new gadget, a car, or for long-term goals like college or a down payment on a house. Explore different savings options like high-yield savings accounts or even investment options to make your money grow.
Spending Wisely
Teenagers are often bombarded with advertising and peer pressure to spend money on the latest trends. However, it’s essential to differentiate between needs and wants. Before making a purchase, consider if it aligns with your budget and if it’s a genuine need or just a fleeting desire.
Debt Management
While it’s best to avoid debt altogether, understanding how credit cards and loans work is crucial. Learn about interest rates and the potential consequences of debt. If you do use credit cards, make sure to use them responsibly by paying off your balance in full each month to avoid accumulating debt.
Earning Money
Earning your own money, even through part-time jobs or side hustles, can provide valuable experience in financial responsibility. It not only gives you a sense of accomplishment but also helps you understand the value of money and the importance of hard work.
The Basics of Budgeting
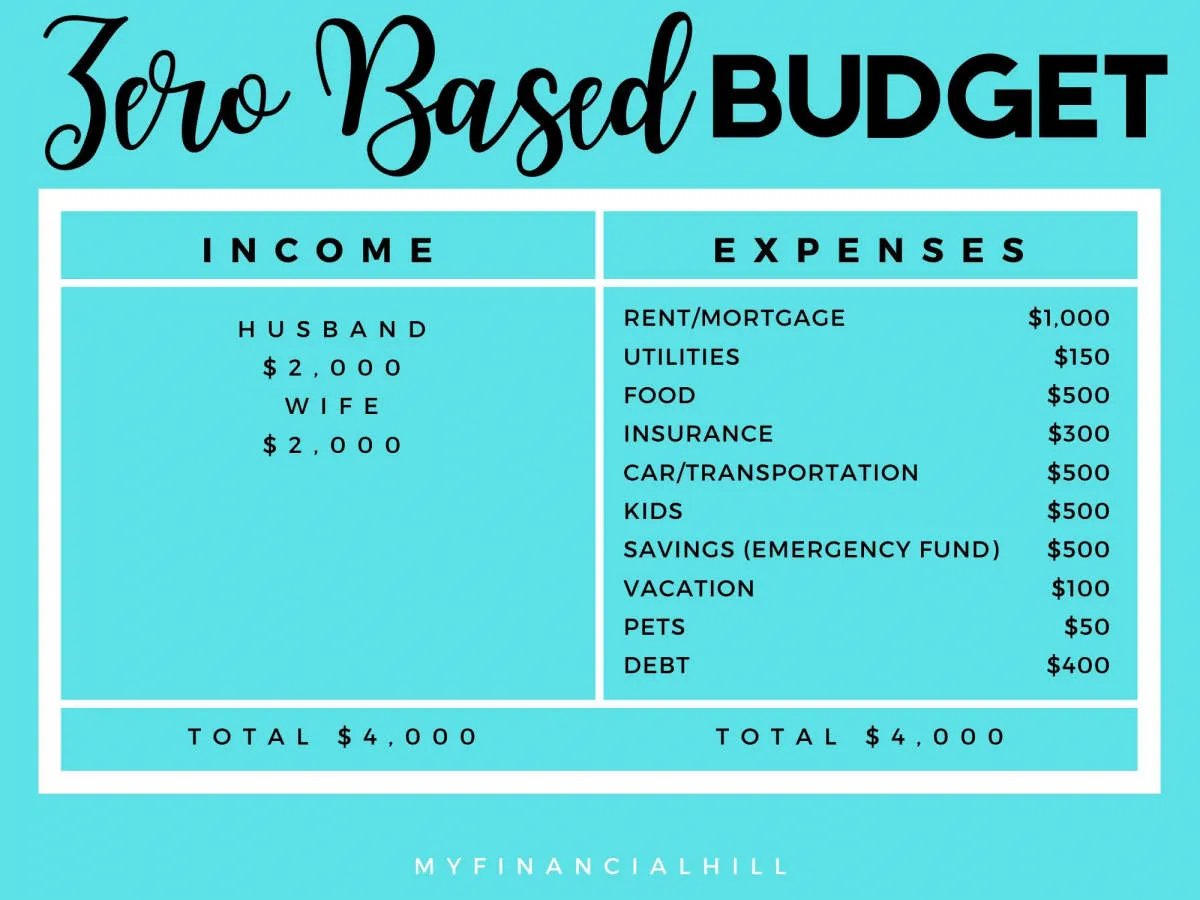
Budgeting might sound like something only adults need to worry about, but understanding the basics early on can set you up for a lifetime of healthy financial habits. It’s all about understanding where your money comes from and where it goes.
1. Tracking Your Income and Expenses
The first step is to figure out how much money you have coming in and going out.
- Income: This could be allowance, money from a part-time job, or gifts.
- Expenses: List everything you spend money on, like snacks, clothes, entertainment, and transportation.
You can track this information in a notebook, a spreadsheet, or using budgeting apps available on your phone.
2. Creating a Budget Plan
Now it’s time to create a plan for your money. Decide how much you want to spend in different categories. For example:
- 50% Needs (food, transportation)
- 30% Wants (entertainment, shopping)
- 20% Savings (future goals)
Adjust these percentages based on your own needs and goals.
3. Setting Financial Goals
Having financial goals gives you something to work towards. Do you want to buy a new phone, save for a car, or go on a trip with friends? Write down your goals and figure out how much you need to save each week or month to reach them.
4. Sticking to Your Budget
The hardest part of budgeting is often sticking to the plan you’ve made. It takes discipline to resist impulse purchases and save for the things that are important to you. Review your budget regularly and make adjustments as needed.
Saving and Investing

Understanding the concepts of saving and investing is crucial for teenagers as they start their financial journey.
Saving: Building a Foundation
Saving involves setting aside a portion of your income for future use. It’s about making conscious spending choices today to secure your financial well-being tomorrow. Here’s why saving is essential:
- Emergencies: Life is full of surprises, and having a savings cushion can help you navigate unexpected expenses like medical bills or car repairs without derailing your finances.
- Short-Term Goals: Whether it’s buying a new phone, a car, or saving for a dream vacation, having specific savings goals can keep you motivated and disciplined.
Investing: Growing Your Money
While saving involves putting money aside, investing puts your money to work. It means using your savings to potentially grow your wealth over time. Here’s why investing is important:
- Beat Inflation: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time. Investing helps your money grow at a rate that can outpace inflation, preserving and even increasing your wealth.
- Long-Term Goals: Investing is crucial for achieving significant life goals, such as funding higher education, buying a house, or securing a comfortable retirement.
The Importance of Credit
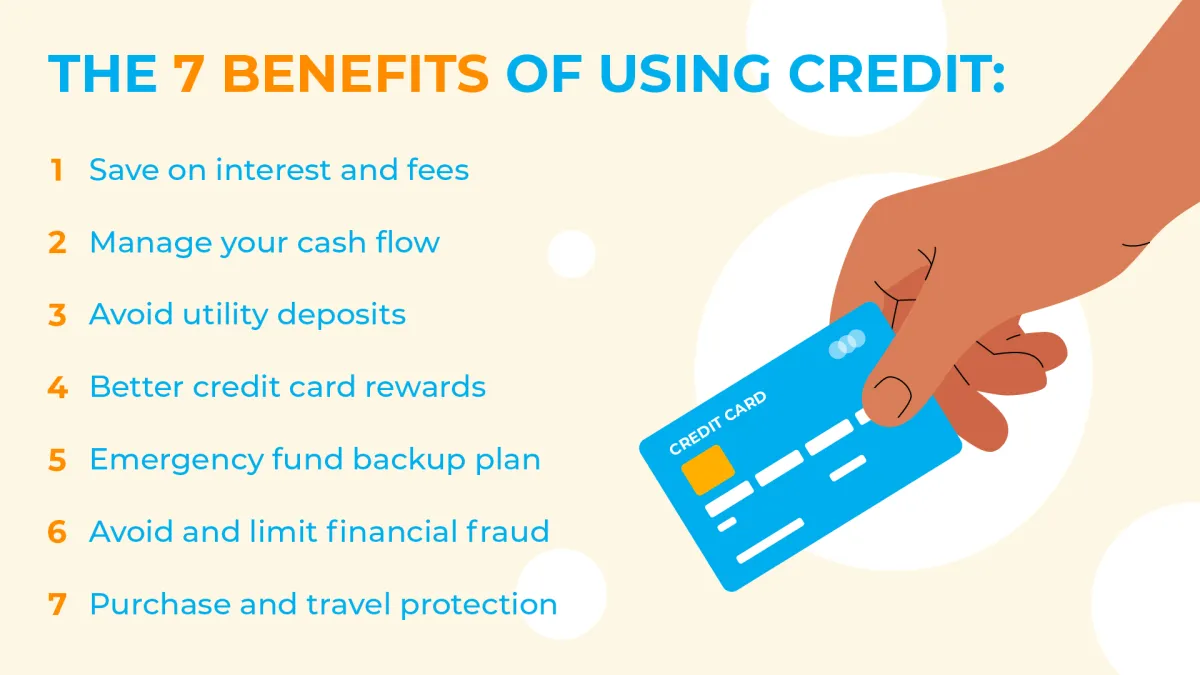
Credit plays a crucial role in achieving financial well-being, making it essential for teenagers to grasp its significance early on. A good credit history opens doors to various financial opportunities and lower interest rates.
Building Credit: Building credit is a gradual process that involves responsibly managing borrowed funds. Teenagers can start by becoming authorized users on a parent’s or guardian’s credit card or opening a secured credit card. By making timely payments and keeping credit card balances low, they demonstrate responsible credit behavior, which is reflected in their credit score.
Impact of Credit: A good credit score unlocks favorable interest rates on loans for significant life events such as purchasing a car or a home. It also impacts other financial aspects, including renting an apartment, securing insurance, or even landing certain jobs. On the other hand, poor credit history can lead to higher interest rates, limited financial options, and potential obstacles in the future.
Understanding Credit Reports and Scores: Learning to read and understand credit reports and credit scores is vital. Teenagers should be aware of the factors influencing their creditworthiness and the importance of regularly checking for inaccuracies.
Managing Debt

Debt can seem like a scary concept, but understanding how it works is crucial for healthy financial habits. Debt itself isn’t always bad – think about things like student loans which can help you invest in your future. The key is to manage debt responsibly and avoid falling into a cycle of debt you can’t get out of.
Here are some essential tips for teenagers to manage debt:
- Understand Credit Cards: Credit cards aren’t free money. They’re a loan you have to pay back, often with interest. Learn about credit limits, interest rates, and the importance of paying your balance on time.
- Avoid Impulse Purchases: Think before you swipe! Ask yourself if you really need something or if you can wait and save up for it instead of putting it on credit.
- Track Your Spending: Use budgeting apps or a simple notebook to monitor where your money is going. This will help you identify areas where you can cut back and avoid unnecessary debt.
- Create a Budget: A budget outlines your income and expenses, showing you how much money you have coming in and where it’s going. This makes it easier to plan for expenses and avoid overspending.
- Emergency Fund: Having money set aside for emergencies means you’re less likely to rely on credit cards if unexpected expenses pop up.
Financial Goal Setting
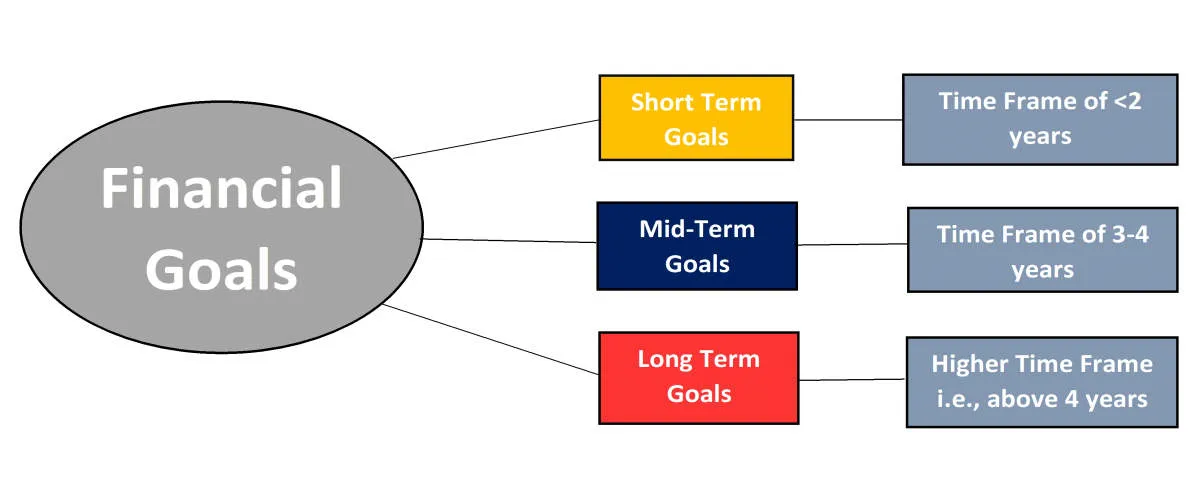
Understanding personal finance is crucial for teenagers as it lays the foundation for a secure financial future. One key aspect of financial literacy is setting financial goals. Setting clear and specific financial goals provides direction and motivation, helping teenagers make informed financial decisions.
Types of Financial Goals for Teenagers:
- Short-Term Goals: These goals can be achieved in a short span of time, typically within a few months. Examples include saving for a new phone, buying concert tickets, or purchasing new clothes.
- Mid-Term Goals: These goals require a longer timeframe, usually a few years. Examples include saving for a car, a down payment on a future apartment, or funding a gap year experience.
- Long-Term Goals: These goals involve significant financial planning and typically take several years or even decades to achieve. Examples include saving for college, purchasing a home, or investing for retirement.
Setting SMART Financial Goals:
To increase the likelihood of achieving financial goals, it’s essential to set SMART goals:
- Specific: Clearly define the goal and what needs to be accomplished.
- Measurable: Quantify the goal with specific amounts and deadlines.
- Attainable: Set realistic goals that are challenging yet achievable.
- Relevant: Align goals with personal values and aspirations.
- Time-Bound: Establish a clear timeframe for achieving the goal.
Tips for Setting Financial Goals:
- Start by identifying what’s important and what you want to achieve financially.
- Break down larger goals into smaller, more manageable steps.
- Create a budget to track income, expenses, and savings progress.
- Explore different savings and investment options.
- Seek guidance from parents, guardians, or financial mentors.
How to Read Financial Statements
Financial statements might seem intimidating at first glance, but they’re essentially just snapshots of a company’s financial health. Understanding the basics of reading them can be a huge advantage in making informed financial decisions.
Here are the three key financial statements you should know:
1. Balance Sheet
The balance sheet gives you a glimpse of what a company owns (assets) and owes (liabilities) at a specific point in time. It also shows you the company’s equity, which is the difference between assets and liabilities.
- Assets: Things the company owns like cash, inventory, and property.
- Liabilities: Money the company owes to others, like loans and accounts payable.
- Equity: What’s left over for the owners of the company after liabilities are paid off.
2. Income Statement
The income statement, also known as the profit and loss statement, shows how much money a company made (revenue) and spent (expenses) over a period of time.
- Revenue: Money earned from selling goods or services.
- Expenses: Costs incurred in generating revenue, such as salaries and rent.
- Net Income: The profit (or loss) after subtracting expenses from revenue.
3. Cash Flow Statement
This statement tracks the movement of cash both in and out of the company over a specific time period. It helps you understand where the company gets its cash and how it’s being used.
- Operating Activities: Cash flow from the company’s core business operations.
- Investing Activities: Cash spent or received from investments, like buying or selling equipment.
- Financing Activities: Cash flow related to debt, equity, and dividends.
Don’t worry about understanding every single detail right away. Start by getting familiar with the basic components of each statement, and over time, you’ll develop a stronger grasp of how to interpret them.
Using Financial Tools

Understanding financial concepts is important, but putting knowledge into action requires using financial tools. Here are some key tools teenagers should become familiar with:
1. Budgeting Apps and Spreadsheets:
Budgeting is the foundation of financial health. Apps and spreadsheets help track income and expenses, set financial goals, and identify areas to save. Many user-friendly budgeting apps are designed specifically for teenagers.
2. Savings Accounts:
Learning to save is crucial. Teens can explore different savings accounts, compare interest rates, and set up automatic savings plans to reach their goals, whether it’s buying a car, a laptop, or saving for college.
3. Checking Accounts and Debit Cards:
A checking account teaches responsible money management. Teens can learn to deposit money, withdraw cash, and track spending using a debit card. This helps them understand the flow of money and practice making payments.
4. Investment Simulators:
While teens might not be ready to invest real money yet, investment simulators provide a risk-free way to learn about the stock market. They can experiment with different investment strategies and understand how investments can grow over time.
5. Financial Literacy Apps and Websites:
Numerous apps and websites are designed specifically to teach teenagers about finance. These platforms offer interactive games, quizzes, and educational content that makes learning about money fun and engaging.
By becoming comfortable with these financial tools, teenagers can develop responsible financial habits early on and set themselves up for a secure financial future.
Building Good Financial Habits

Building good financial habits as a teenager sets the stage for a lifetime of financial well-being. It’s much easier to form good habits early on than to try to break bad ones later in life. Here are some key habits to cultivate:
- Budgeting: Learn how to track your income and expenses. This will help you understand where your money is going and identify areas where you can save. There are many budgeting apps available, or you can use a simple spreadsheet.
- Saving: Make it a habit to save a portion of every dollar you receive. This could be from allowance, gifts, or part-time jobs. Aim to have a specific savings goal in mind, whether it’s for a new phone, college, or a future car.
- Smart Spending: Before making a purchase, especially a large one, take time to research and compare prices. Learn to differentiate between needs and wants, and prioritize your spending accordingly.
- Earning: Explore opportunities to earn money, such as part-time jobs, freelance work, or starting a small business. Earning money provides valuable experience and teaches you about responsibility and work ethic.
- Investing: Learn about different investment options, like stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. Even small investments, made consistently over time, can grow significantly due to the power of compound interest.
Seeking Financial Advice

As teenagers start to earn and manage their own money, it can be overwhelming to make smart financial decisions. This is where seeking financial advice becomes crucial.
Don’t be afraid to ask for help. Talk to your parents, guardians, or a trusted adult about money matters. They can share their experiences and offer guidance based on your specific situation.
Consider consulting a financial advisor. A financial advisor can provide personalized advice on budgeting, saving, investing, and planning for the future. They can help you set realistic financial goals and develop strategies to achieve them.
Remember:
- It’s never too early to start learning about personal finance and seek guidance.
- Asking for help is a sign of responsibility, not weakness.
- A little financial advice can go a long way in securing your financial future.
Conclusion
Financial literacy for teenagers is essential for their future financial well-being and decision-making skills.

