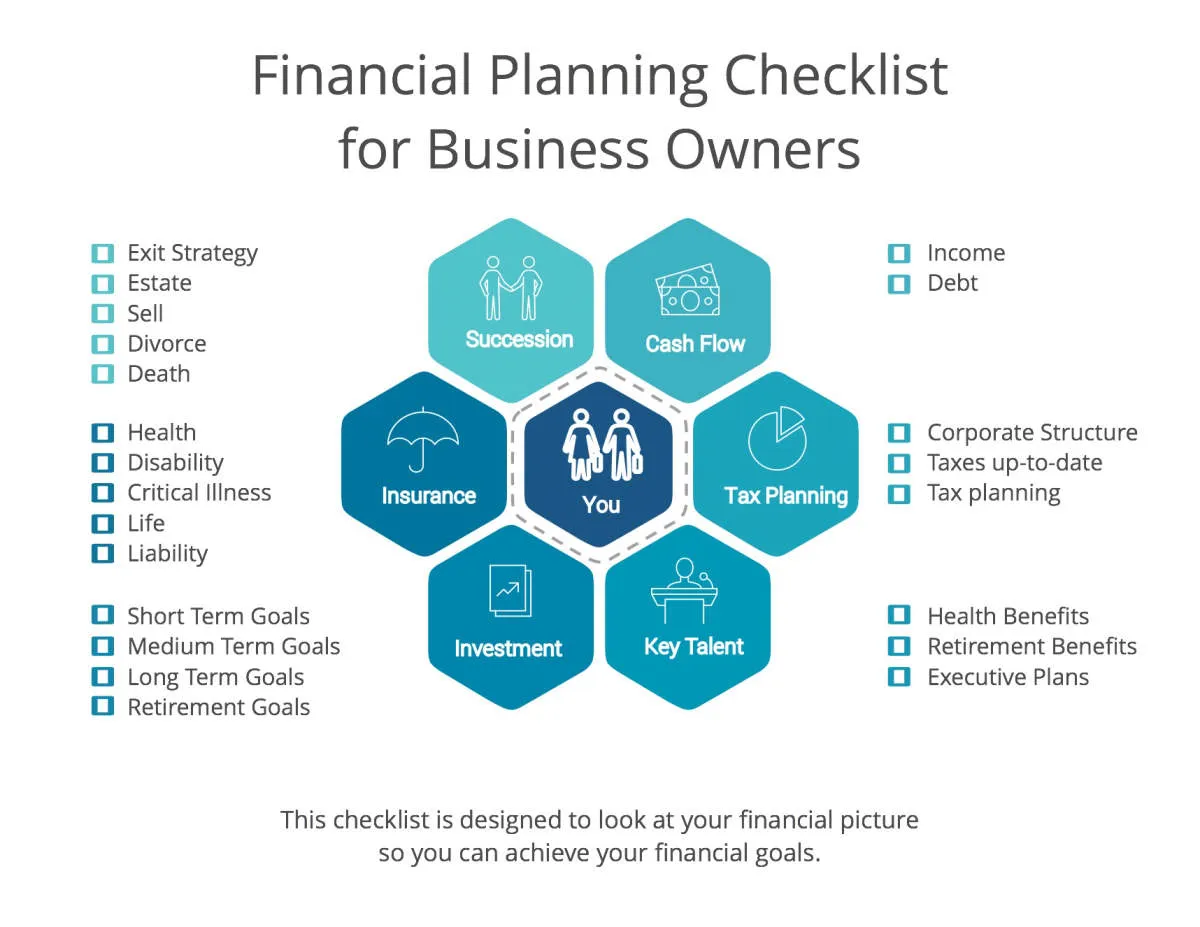
Learn how to develop a comprehensive financial plan to ensure the success of your business. This article covers essential steps, such as budgeting, forecasting, and investments, to help you achieve your financial goals.
Understanding Financial Planning

Financial planning is a crucial aspect of running a successful business. It involves analyzing your current financial situation, setting financial goals, and creating a roadmap to achieve those goals. A well-structured financial plan acts as a guide, helping you make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and navigate the financial complexities of your business.
Key elements of financial planning for your business include:
- Assessing your current financial health: This involves analyzing your income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements to understand your business’s financial performance and position.
- Defining your financial goals: Identify both short-term and long-term financial objectives for your business, such as revenue targets, profitability margins, or expansion plans.
- Developing financial projections: Create forecasts of your future financial performance, including projected income, expenses, and cash flow.
- Creating a budget: Establish a detailed plan outlining your expected income and expenses over a specific period, enabling you to track performance and make necessary adjustments.
- Determining funding sources: Identify potential sources of funding to support your business operations and growth, whether through loans, investments, or other avenues.
- Monitoring and evaluating performance: Regularly review your financial results, compare them against your plan, and make informed adjustments to your strategies as needed.
By engaging in a comprehensive financial planning process, you can gain a clear understanding of your business’s financial situation, anticipate future challenges, and make informed decisions to drive profitability and sustainability.
Setting Business Goals

Before diving into the nitty-gritty of financial forecasting and budgeting, you need to establish clear, concise, and measurable business goals. These goals will act as the compass guiding your financial plan and dictating where your resources should be allocated.
Consider these key aspects when setting your business goals:
- Specificity: Avoid vague goals like “increase sales.” Instead, aim for specific targets like “increase online sales by 20% within the next quarter.”
- Measurability: Ensure your goals can be quantified. This allows you to track progress and make adjustments to your financial plan as needed.
- Attainability: While ambition is encouraged, set realistic goals that are achievable within your resources and market conditions.
- Relevance: Each goal should align with your overall business vision and mission. This ensures you’re moving in the right direction and making strategic decisions.
- Time-bound: Set deadlines for achieving your goals. This creates a sense of urgency and provides a clear timeframe for your financial projections.
Examples of common business goals that will directly influence your financial plan include:
- Revenue generation and growth targets
- Market share expansion
- Product development and innovation
- Geographic expansion or new market entry
- Improving operational efficiency and profitability
By clearly defining your business goals, you’ll be able to translate them into concrete financial objectives within your plan. This ensures that your financial resources are strategically aligned to support your overall business growth and success.
Creating a Budget

A budget is a financial plan that outlines your business’s expected income and expenses over a specific period. It’s a crucial component of your financial plan, acting as a roadmap for your business’s financial health.
Steps to Create a Business Budget:
- Estimate Income: Forecast your revenue streams. Be realistic and consider historical data, market trends, and sales projections.
- Identify and Categorize Expenses: List all your business expenses. This can include fixed costs (rent, salaries) and variable costs (raw materials, marketing).
- Use Budgeting Methods: Implement budgeting methods like zero-based budgeting (justify every dollar) or the 50/30/20 rule (allocate 50% for needs, 30% for wants, and 20% for savings or debt repayment). Tailor these methods to your business needs.
- Project Cash Flow: Analyze the timing of your income and expenses. This will help you anticipate potential shortfalls and ensure you have enough liquidity to cover costs.
- Track and Adjust Regularly: Regularly review and compare your actual financial performance against your budget. Identify variances, understand their causes, and make necessary adjustments to your budget and business operations.
Key Considerations:
- Be realistic with your projections. It’s better to underestimate income and overestimate expenses.
- Prioritize essential expenses and look for areas to cut costs.
- Build in a contingency fund for unexpected expenses.
Creating a budget may seem daunting, but it’s an essential investment in your business’s success. By carefully planning your finances, you’ll gain better control over your cash flow, make informed decisions, and increase your chances of achieving your financial goals.
Managing Cash Flow

Managing cash flow is crucial for any business, big or small. It’s about ensuring your business has enough cash on hand to cover its day-to-day expenses while also having enough to invest in growth opportunities. Here’s how to effectively manage your business’s cash flow:
1. Accurate Financial Forecasting
Start by creating realistic and detailed financial forecasts. This involves projecting future income and expenses, ideally for the next 12 months. Consider seasonality, potential market fluctuations, and any planned expenses like new hires or marketing campaigns.
2. Track Your Cash Inflows and Outflows
Maintain a meticulous record of all incoming and outgoing cash. Utilize accounting software or spreadsheets to monitor where your money is coming from (sales, investments) and where it’s being spent (rent, payroll, inventory). This clarity helps identify potential cash flow gaps.
3. Optimize Your Invoicing and Payment Processes
Ensure you invoice promptly and accurately. Explore offering early payment discounts to incentivize customers. For your expenses, negotiate favorable payment terms with vendors. Consider options like extending payment deadlines or arranging payment plans where feasible.
4. Build a Cash Flow Cushion
Unexpected expenses and market dips are inevitable. Having a cash reserve acts as a buffer to navigate these uncertainties without jeopardizing your business operations. Aim to have 3-6 months’ worth of operating expenses saved as a financial safety net.
5. Explore Funding Options
If you anticipate needing additional capital for expansion or to cover short-term gaps, research funding options. This might include lines of credit, short-term loans, or invoice financing. Be sure to compare interest rates and terms to find the most favorable solution.
6. Regularly Review and Adjust
Cash flow management is not a one-time task. Regularly review your financial forecasts and actual cash flow statements. Compare your projections to real-time data and make necessary adjustments to your budget and operations. This proactive approach helps you stay ahead of potential issues.
Investing in Your Business

Investing in your business is a critical aspect of your financial plan. This encompasses allocating resources to fuel growth, improve efficiency, and enhance your competitive edge. Here’s how to strategically approach investments:
Identify Growth Opportunities
Analyze your business to pinpoint areas with the highest potential for return. This could include:
- Product Development: Investing in research and development to create new products or improve existing ones.
- Marketing and Sales: Expanding your reach to new customers through various marketing channels.
- Technology: Upgrading your systems or software to boost productivity and streamline operations.
- Employee Training: Enhancing the skills and knowledge of your workforce.
- Expansion: Opening new locations, entering new markets, or scaling up production.
Determine Investment Needs
Once you’ve identified opportunities, quantify the financial resources required for each. This involves researching costs, obtaining quotes, and projecting potential returns on investment (ROI).
Explore Funding Sources
Consider various financing options to fund your investments. Some possibilities include:
- Business Loans: Traditional bank loans or Small Business Administration (SBA) loans.
- Equity Financing: Seeking investments from venture capitalists, angel investors, or through crowdfunding.
- Business Lines of Credit: Accessing flexible credit for short-term needs.
- Grants: Exploring government grants or private foundation funding opportunities.
- Bootstrapping: Utilizing personal savings or reinvesting profits back into the business.
Develop an Investment Strategy
Prioritize your investments based on their potential impact, alignment with your business goals, and available resources. Create a timeline for each investment, outlining key milestones and expected outcomes.
Monitor and Evaluate
Regularly track the performance of your investments against your projected ROI and adjust your strategy as needed. Continuously assess the market, identify emerging opportunities, and remain adaptable to ensure your business stays competitive.
Using Financial Tools

Creating a financial plan for your business involves more than just jotting down some numbers. To effectively manage your finances and make informed decisions, utilizing financial tools is essential. These tools provide structure, insights, and the ability to track your progress over time.
Commonly Used Financial Tools:
- Budgeting Software: Tools like QuickBooks, Xero, and Mint help you create and monitor budgets, track expenses, and generate financial reports. These tools simplify financial management and provide a clear overview of your business’s financial health.
- Financial Spreadsheets: Spreadsheets (like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets) are incredibly versatile for financial planning. You can create pro forma financial statements, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and perform sensitivity analyses to assess different scenarios.
- Cash Flow Forecasting Tools: Predicting future cash flow is crucial for any business. Tools specifically designed for cash flow forecasting help you anticipate surpluses and shortfalls, enabling you to make informed decisions about investments, borrowing, and spending.
- Invoicing and Expense Tracking Software: Streamline your billing and expense management with tools like FreshBooks, Zoho Invoice, or Expensify. These platforms automate tasks like creating and sending invoices, tracking payments, and categorizing expenses.
- Financial Reporting Software: Generate professional financial reports that provide insights into your business’s performance. Tools like Fathom or Tableau offer customizable dashboards, visualizations, and reporting features.
Benefits of Using Financial Tools:
- Improved Accuracy: Reduce the risk of manual errors and increase the accuracy of your financial data.
- Time Savings: Automate tasks like data entry, invoice generation, and report creation, freeing up your time for strategic planning.
- Data-Driven Insights: Gain valuable insights into your business’s financial performance through detailed reports, charts, and analysis.
- Better Decision-Making: Make informed decisions about pricing, investments, and resource allocation based on accurate and up-to-date financial information.
- Increased Accountability: Establish clear financial records and track progress towards your goals, promoting accountability within your business.
When selecting financial tools, consider your business’s specific needs, budget, and technical expertise. Many tools offer free trials or freemium plans, allowing you to test them before committing.
Reviewing and Adjusting Your Financial Plan

Creating a financial plan isn’t a “set it and forget it” endeavor. The business world is dynamic, and your plan needs to adapt to internal and external changes. Here’s how to approach the crucial task of review and adjustment:
Set a Review Schedule
Don’t wait for things to go wrong before revisiting your plan. Establish a regular review schedule. Consider quarterly reviews for businesses in early stages or experiencing rapid growth, and annual reviews for more established entities.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Identify and track KPIs that align with your financial goals. These could include:
- Revenue growth
- Gross and net profit margins
- Cash flow
- Customer acquisition cost
Regularly compare your actual performance against these KPIs to identify areas for improvement or adjustment.
Market Analysis
Stay informed about industry trends, competitor activities, and changes in the economic landscape. Factors like new regulations, technological advancements, or shifts in consumer behavior can significantly impact your financial projections.
Flexibility and Adaptation
Be prepared to make adjustments to your plan as needed. This could involve:
- Revising sales forecasts
- Adjusting pricing strategies
- Exploring new funding sources
- Re-evaluating operational expenses
Seeking Professional Guidance
Consider consulting with a financial advisor or accountant, especially when facing complex financial decisions or significant market shifts. Their expertise can provide valuable insights and help you navigate challenges effectively.
Seeking Professional Advice

While creating a basic financial plan for your business is possible on your own, seeking advice from financial professionals can provide invaluable insights and guidance. These experts can help you:
- Identify and leverage tax benefits: Tax laws can be complex and vary significantly based on your industry and location. A qualified accountant or tax advisor can help you optimize your tax strategy and minimize your liabilities.
- Develop a robust financial model: Financial advisors can help you create detailed financial projections, cash flow statements, and other essential financial models, allowing for more accurate forecasting and decision-making.
- Secure funding: Whether you’re seeking venture capital, angel investors, or bank loans, financial advisors can connect you with potential funders and help you present a compelling business case.
- Navigate complex financial instruments: Depending on your business needs, you might consider utilizing financial instruments like hedging strategies or derivatives. A financial advisor can guide you through the complexities of these instruments and mitigate potential risks.
- Plan for the future: Beyond immediate financial concerns, advisors can help you plan for long-term sustainability, including succession planning, exit strategies, and retirement contributions.
Choosing the right financial professionals is crucial. Look for individuals or firms with experience in your industry and a proven track record of success. Don’t hesitate to schedule consultations with multiple advisors to find the best fit for your business needs.
Preparing for Financial Emergencies

Even with the most carefully crafted financial plan, unexpected events can and will occur. That’s why anticipating and preparing for financial emergencies is crucial for the long-term stability of your business.
Here are key steps to consider:
1. Establish an Emergency Fund
Just like personal finances, businesses need a safety net. Aim to build an emergency fund that can cover 3-6 months of operating expenses. This fund acts as a buffer during unexpected downturns, allowing you to cover essential costs without going into debt.
2. Identify Potential Risks
Every business faces unique risks. Spend time identifying potential financial emergencies specific to your industry and business model. This could include:
- Economic downturns
- Industry disruptions
- Natural disasters
- Loss of key clients or suppliers
- Cybersecurity breaches
3. Develop Contingency Plans
Don’t wait for an emergency to happen before figuring out what to do. Develop contingency plans for each identified risk. This could involve:
- Securing alternative suppliers
- Diversifying your customer base
- Having a crisis communication plan
- Implementing robust data backup and recovery systems
4. Review Insurance Coverage
Regularly review your business insurance policies to ensure they adequately cover potential risks. Consider scenarios like property damage, liability lawsuits, and business interruption when assessing your coverage needs.
5. Maintain Financial Flexibility
Strive for a balance between leveraging debt for growth and retaining financial flexibility. Having access to credit lines or alternative financing options can be invaluable during emergencies.
By proactively planning for financial emergencies, you can mitigate their impact and ensure your business weathers the storm. Remember, a well-prepared business is a resilient one.
Understanding Financial Statements
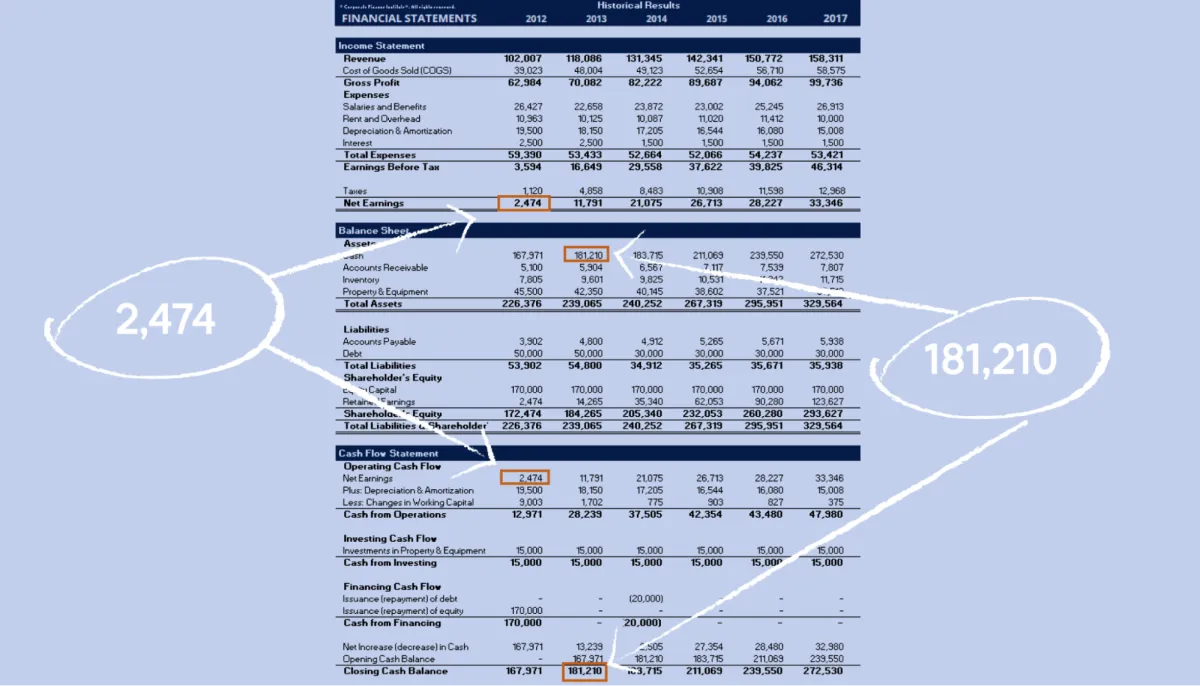
Before diving into the specifics of creating a financial plan, it’s crucial to grasp the language of business finance—financial statements. These statements provide a snapshot of your business’s financial health and performance, forming the bedrock of any sound financial plan.
There are three primary financial statements you need to be familiar with:
-
Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement)
The income statement tracks your business’s revenues and expenses over a specific period, typically a quarter or a year. It reveals your profitability by showing whether you generated a profit or incurred a loss.
Key components include:
- Revenue: Income generated from your primary business activities.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Direct costs associated with producing goods or services.
- Gross Profit: Revenue minus COGS.
- Operating Expenses: Costs of running your business, such as rent, salaries, and marketing.
- Net Income (Profit/Loss): The bottom line, calculated as Revenue – COGS – Operating Expenses.
-
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of your business’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. It follows the accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity.
Key components include:
- Assets: What your business owns, such as cash, inventory, and equipment.
- Liabilities: What your business owes to others, like loans and accounts payable.
- Equity: The owner’s stake in the business, representing the difference between assets and liabilities.
-
Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement tracks the movement of cash both into and out of your business over a specific period. It provides a clear picture of your business’s liquidity—its ability to meet short-term obligations.
Key components include:
- Operating Activities: Cash flow from core business operations.
- Investing Activities: Cash flow from investments, such as buying or selling assets.
- Financing Activities: Cash flow from debt, equity, and dividends.
Understanding these financial statements is paramount for creating a successful financial plan. They provide the insights needed to set realistic goals, make informed decisions, and track your business’s progress over time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, creating a financial plan is crucial for the success of your business. By setting clear goals, tracking expenses, and regularly reviewing your plan, you can ensure financial stability and growth.