Learn how to streamline your business finances with our expert tips for efficient financial management. Discover strategies to optimize your budget, maximize profits, and ensure long-term sustainability for your company.
Creating a Financial Plan

A comprehensive financial plan is the backbone of efficient business financial management. It acts as a roadmap, guiding your business towards financial stability and growth.
Here’s what to consider when crafting your financial plan:
1. Set Clear Financial Goals
Define both short-term and long-term financial objectives. Are you aiming for rapid expansion, increased profitability, or greater market share? Having specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals will provide direction for your financial strategies.
2. Analyze Your Current Financial Situation
Before charting a course forward, you need to understand your starting point. Conduct a thorough analysis of your current financial statements, including your balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. Identify areas of strength and weakness, and assess your current financial health.
3. Develop a Budget
A budget is a crucial tool for financial planning, outlining projected income and expenses over a specific period. It helps to monitor cash flow, control costs, and allocate resources effectively. Ensure your budget aligns with your overarching financial goals.
4. Explore Funding Options
Whether you’re just starting or looking to expand, consider potential sources of funding. This could include bootstrapping, seeking investments, applying for loans, or exploring crowdfunding options. Understand the terms, interest rates, and repayment schedules associated with each option.
5. Plan for Taxes
Tax planning is an integral part of financial management. Consult with a tax professional to understand your tax obligations, explore legal deductions and credits, and optimize your tax strategy.
6. Establish Financial Controls
Implement internal controls to safeguard your assets, prevent fraud, and ensure accurate financial reporting. These controls might include segregation of duties, authorization procedures, and regular audits.
7. Regularly Review and Adjust
Your financial plan should not be static. Regularly review your progress, assess the effectiveness of your strategies, and make adjustments as needed. Factor in market changes, economic conditions, and internal business developments when revising your plan.
Managing Cash Flow

Maintaining healthy cash flow is crucial for any business’s survival and growth. It refers to the movement of money in and out of your business. Efficient cash flow management involves:
1. Forecasting Cash Flow
Accurately predict your business’s future cash inflows and outflows. This involves analyzing historical data, considering seasonality, and anticipating future expenses and income. Accurate forecasting helps you identify potential shortfalls and surpluses, allowing for proactive financial planning.
2. Optimizing Accounts Receivable
Timely collection of receivables is critical. Implement strategies to expedite payments from customers, such as offering early payment discounts, setting clear payment terms, and using invoicing software for automated reminders.
3. Managing Accounts Payable
Negotiate favorable payment terms with suppliers while ensuring timely payments to maintain good relationships. Consider options such as extending payment deadlines or taking advantage of early payment discounts when possible.
4. Controlling Operational Costs
Regularly review your expenses and identify areas for cost reduction. Negotiate better deals with suppliers, explore more cost-effective alternatives, and eliminate unnecessary expenses without compromising the quality of your products or services.
5. Having a Cash Reserve
Maintain a cash reserve to cover unexpected expenses or downturns in business. Aim to have enough cash on hand to cover 3-6 months of operating expenses. This safety net provides financial stability and peace of mind.
6. Using Cash Flow Management Tools
Leverage technology to your advantage. Various software and tools can automate invoicing, track expenses, and provide real-time insights into your cash flow, simplifying financial management.
Reducing Business Expenses

Keeping business expenses in check is crucial for maximizing profitability and ensuring long-term sustainability. There are many areas businesses can focus on to reduce unnecessary spending and improve their bottom line.
Negotiate with Suppliers
Don’t be afraid to negotiate better rates with your suppliers, especially if you’ve been a loyal customer for a long time. Explore alternative vendors to compare pricing and services. Building strong relationships with suppliers can open doors to discounts, favorable payment terms, and other cost-saving opportunities.
Embrace Technology
Leveraging technology can lead to significant cost reductions in various areas. Explore cloud-based solutions for accounting, customer relationship management (CRM), and project management, as they often offer more affordable pricing compared to traditional software options.
Go Paperless
Transitioning to a paperless office not only benefits the environment but also saves money on printing, paper, ink, and storage costs. Encourage digital communication and document sharing whenever possible.
Review Subscriptions and Services
Regularly evaluate the necessity of your business subscriptions and services. Identify and eliminate any redundant or underutilized subscriptions to avoid unnecessary expenses.
Outsource Strategically
Outsourcing certain business functions, such as payroll, accounting, or customer support, can be more cost-effective than hiring full-time employees. By outsourcing, you can access specialized expertise without the overhead costs associated with benefits and training.
Reduce Energy Consumption
Implement energy-saving practices in your workplace to lower utility bills. Simple changes like using energy-efficient lighting, adjusting thermostat settings, and encouraging employees to conserve energy can make a difference.
Explore Remote Work Options
Offering remote work options to your employees can reduce overhead costs associated with office space, utilities, and supplies. Additionally, remote work arrangements can lead to increased productivity and employee satisfaction.
Investing in Your Business

Wise financial management extends beyond managing day-to-day expenses. Investing in your business is crucial for long-term growth and profitability. This could take various forms, each offering a different return on investment:
1. Expanding Your Operations:
Investing in new equipment, technology, or larger premises can boost your production capacity, efficiency, and overall reach. Analyze your business needs and market trends to identify expansion opportunities that align with your growth strategy.
2. Developing Your Workforce:
Your employees are your most valuable asset. Investing in training programs, professional development opportunities, and competitive compensation packages can increase employee skills, motivation, and retention. This leads to improved productivity, innovation, and customer satisfaction.
3. Marketing and Customer Acquisition:
Reaching new customers and solidifying your brand presence requires strategic investment. Allocate resources towards effective marketing campaigns, digital advertising, content creation, and public relations. Track your marketing ROI to optimize campaigns and maximize your reach.
4. Research and Development:
Staying ahead of the curve requires continuous innovation. Investing in research and development allows you to create new products or services, improve existing offerings, and adapt to evolving customer needs. This proactive approach keeps your business competitive and positions you as a market leader.
Using Financial Tools

In today’s digital age, a plethora of financial tools can significantly enhance your business’s financial management. These tools can automate tasks, provide insightful reports, and streamline financial processes, freeing up your time to focus on strategic decision-making.
1. Accounting Software:
Investing in robust accounting software is non-negotiable. Options range from basic cloud-based solutions to comprehensive enterprise-level platforms. Look for features like:
- Income and expense tracking
- Invoicing and billing
- Financial reporting (balance sheets, income statements, cash flow statements)
- Bank reconciliation
- Inventory management
2. Budgeting and Forecasting Tools:
Creating realistic budgets and accurate financial forecasts is crucial for any business. Dedicated software can help you:
- Develop comprehensive budgets
- Track performance against budget
- Generate financial projections based on historical data and trends
- Perform scenario analysis to assess potential outcomes
3. Expense Tracking Apps:
Keeping track of business expenses is vital for tax purposes and expense management. Mobile apps and online platforms make it easy to:
- Log expenses on the go
- Scan receipts and attach them to expense entries
- Categorize expenses for analysis
- Generate expense reports
4. Financial Dashboard and Reporting Software:
Visualizing your financial data is key to gaining insights and making informed decisions. Financial dashboards and reporting tools can:
- Provide real-time overviews of your financial health
- Create customizable reports and charts
- Track key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Identify trends and patterns in your financial data
Reviewing Financial Statements

Regularly reviewing your financial statements is crucial for maintaining a clear understanding of your business’s financial health. It allows you to identify trends, spot potential problems early on, and make informed decisions about your business’s future. Here’s what you should focus on:
1. Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement)
This statement shows your business’s revenues, expenses, and resulting profit or loss over a specific period. Key points to review include:
- Revenue Trends: Is revenue increasing, decreasing, or stagnant? Understanding why is crucial.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Analyze fluctuations in COGS in relation to revenue changes.
- Operating Expenses: Identify areas where costs are rising and explore opportunities for optimization.
- Net Income: Assess the overall profitability of your business. Is it meeting your expectations?
2. Balance Sheet
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of your business’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a particular point in time. Focus on:
- Assets: Track the value of what your business owns (cash, inventory, equipment).
- Liabilities: Monitor what your business owes to others (loans, accounts payable).
- Equity: Understand the value of the owner’s stake in the business.
- Working Capital: Calculate working capital (current assets minus current liabilities) to assess short-term liquidity.
3. Cash Flow Statement
This statement illustrates the movement of cash both into and out of your business over a period. It’s essential to analyze:
- Operating Activities: Track cash generated or used in your core business operations.
- Investing Activities: Monitor cash flow related to investments, such as buying or selling assets.
- Financing Activities: Analyze cash flow from debt, equity, and dividends.
4. Financial Ratios
Utilize key financial ratios to gain deeper insights into your business’s performance. Some important ratios include:
- Profitability Ratios (e.g., gross profit margin, net profit margin)
- Liquidity Ratios (e.g., current ratio, quick ratio)
- Solvency Ratios (e.g., debt-to-equity ratio)
- Efficiency Ratios (e.g., inventory turnover, accounts receivable turnover)
Setting Financial Goals
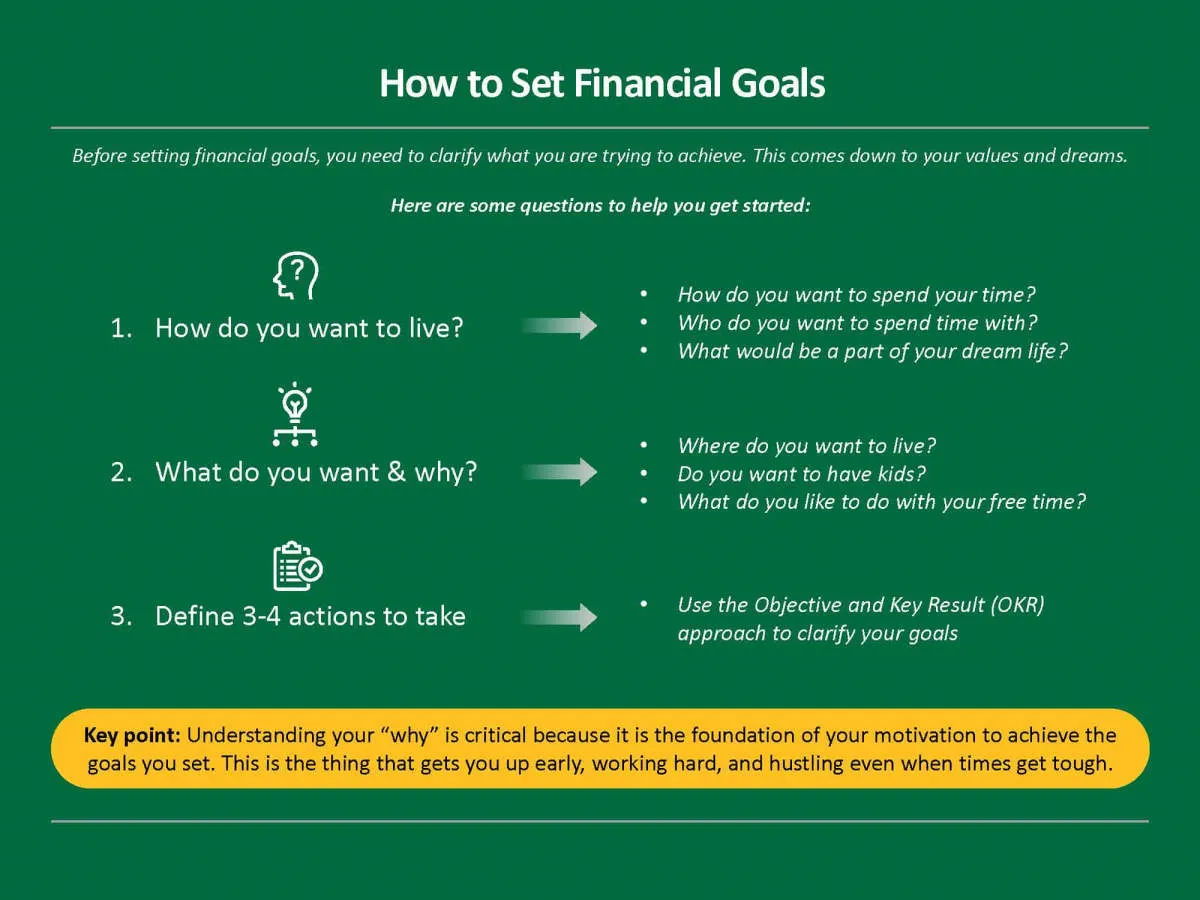
Setting clear and defined financial goals is the bedrock of efficient business financial management. Without well-defined targets, businesses can easily fall into the trap of reactive financial decision-making, leaving them vulnerable to unexpected expenses and missed opportunities.
The Importance of Specificity: When setting financial goals, avoid vague aspirations like “increase profitability.” Instead, aim for specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. For instance, rather than just “increase sales,” a SMART goal would be “increase sales by 15% in the next quarter.”
Types of Financial Goals: Businesses should focus on setting goals across various financial aspects. Some key areas include:
- Revenue Generation: Targets for sales, customer acquisition, or new product launches.
- Cost Management: Goals for reducing operational expenses, optimizing inventory, or improving cash flow.
- Profitability: Targets for gross profit margin, net profit margin, or return on investment (ROI).
- Funding and Investment: Goals related to securing funding, managing debt, or making strategic investments.
Aligning Goals with Business Strategy: Financial goals should not exist in isolation. They must align with the overall business strategy to ensure all efforts contribute to the company’s long-term vision.
Regular Review and Adjustment: Setting goals is not a one-time exercise. Businesses must regularly review their progress, analyze deviations from targets, and make necessary adjustments based on internal performance and external market factors.
Building an Emergency Fund

Unexpected events happen, and businesses need to be prepared. An emergency fund acts as a financial cushion to cover unforeseen expenses and mitigate the impact of crises. These can range from sudden equipment failures and legal disputes to economic downturns impacting sales.
How much should you save? Aim for three to six months worth of essential business expenses. This includes rent, utilities, payroll, inventory, and loan payments. The amount will vary depending on the industry, business size, and risk factors.
Where to keep your emergency fund: Accessibility is key. Choose a high-yield savings account or a money market account that allows for easy withdrawals when needed. Avoid investing these funds in volatile assets like stocks, as market fluctuations could hinder your access to funds during an emergency.
Tips for building your emergency fund:
- Start small: Even setting aside a small amount each week adds up over time.
- Automate transfers: Set up recurring transfers from your business checking account to your emergency fund account.
- Treat it as a non-negotiable expense: Just like rent and payroll, make contributions to your emergency fund a priority.
- Replenish after use: If you need to dip into your emergency fund, prioritize replenishing it as soon as possible.
Seeking Professional Advice

While this article provides a good starting point for managing your business finances, seeking advice from qualified professionals is crucial for long-term success. Financial experts can provide tailored strategies and insights that general advice cannot replicate.
Who Should You Consult?
Consider reaching out to professionals such as:
- Certified Public Accountants (CPAs): CPAs can assist with various financial tasks, including tax preparation, financial statement audits, and general financial advice.
- Certified Financial Planners (CFPs): CFPs specialize in areas like retirement planning, investment management, and estate planning, making them valuable assets for long-term financial strategies.
- Bookkeepers: Bookkeepers can handle your daily financial transactions, ensuring accurate record-keeping and freeing up your time to focus on core business operations.
Benefits of Professional Advice
Seeking professional financial advice offers numerous benefits, including:
- Tax Optimization: Professionals can help you take advantage of relevant tax deductions and credits, minimizing your tax liabilities legally.
- Strategic Financial Planning: Experts can help you develop a comprehensive financial plan tailored to your business goals, encompassing budgeting, forecasting, and risk management.
- Objective Insights: Financial professionals offer an unbiased perspective on your finances, identifying potential problems and opportunities you might overlook.
Remember, investing in professional advice is an investment in your business’s financial health and long-term sustainability.
Understanding Business Taxes

Navigating the world of business taxes is crucial for efficient financial management. Failing to meet your tax obligations can lead to penalties and legal issues, while overpaying can hinder your business’s growth. Here’s what you need to know:
1. Determine Your Business Structure:
Your business structure (sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, corporation) dictates your tax responsibilities. Each structure has its own tax forms, deadlines, and advantages. Consult with a tax professional to determine the best fit for your business.
2. Understand Different Tax Types:
Businesses face various taxes, including:
- Income tax: Levied on profits earned by your business.
- Self-employment tax: Applicable to sole proprietorships and partnerships, covering Social Security and Medicare.
- Sales tax: Collected on goods and services sold, varying by location.
- Payroll tax: Deducted from employee wages, covering Social Security, Medicare, and unemployment.
- Property tax: Levied on business property, such as land and buildings.
3. Keep Accurate Financial Records:
Maintaining organized and detailed financial records is crucial for accurate tax filing. Utilize accounting software or hire a bookkeeper to track income, expenses, deductions, and tax-related documents.
4. Explore Tax Deductions and Credits:
Numerous tax deductions and credits are available to businesses, potentially reducing your tax liability. Common deductions include expenses related to rent, utilities, salaries, marketing, and office supplies. Research available options or consult with a tax advisor to maximize your deductions.
5. Consider Estimated Taxes:
If you expect to owe a significant amount of taxes, the IRS may require you to make estimated tax payments throughout the year. This is common for freelancers, independent contractors, and businesses with fluctuating income.
6. Seek Professional Guidance:
Tax laws are complex and ever-changing. Consulting with a qualified tax professional, such as a Certified Public Accountant (CPA), can provide invaluable guidance tailored to your business’s specific needs. They can help you optimize your tax strategy, ensure compliance, and address any tax-related concerns.
Conclusion
In conclusion, implementing effective financial management practices is crucial for the success and sustainability of any business. By following these tips, companies can enhance their financial health and achieve long-term growth.

