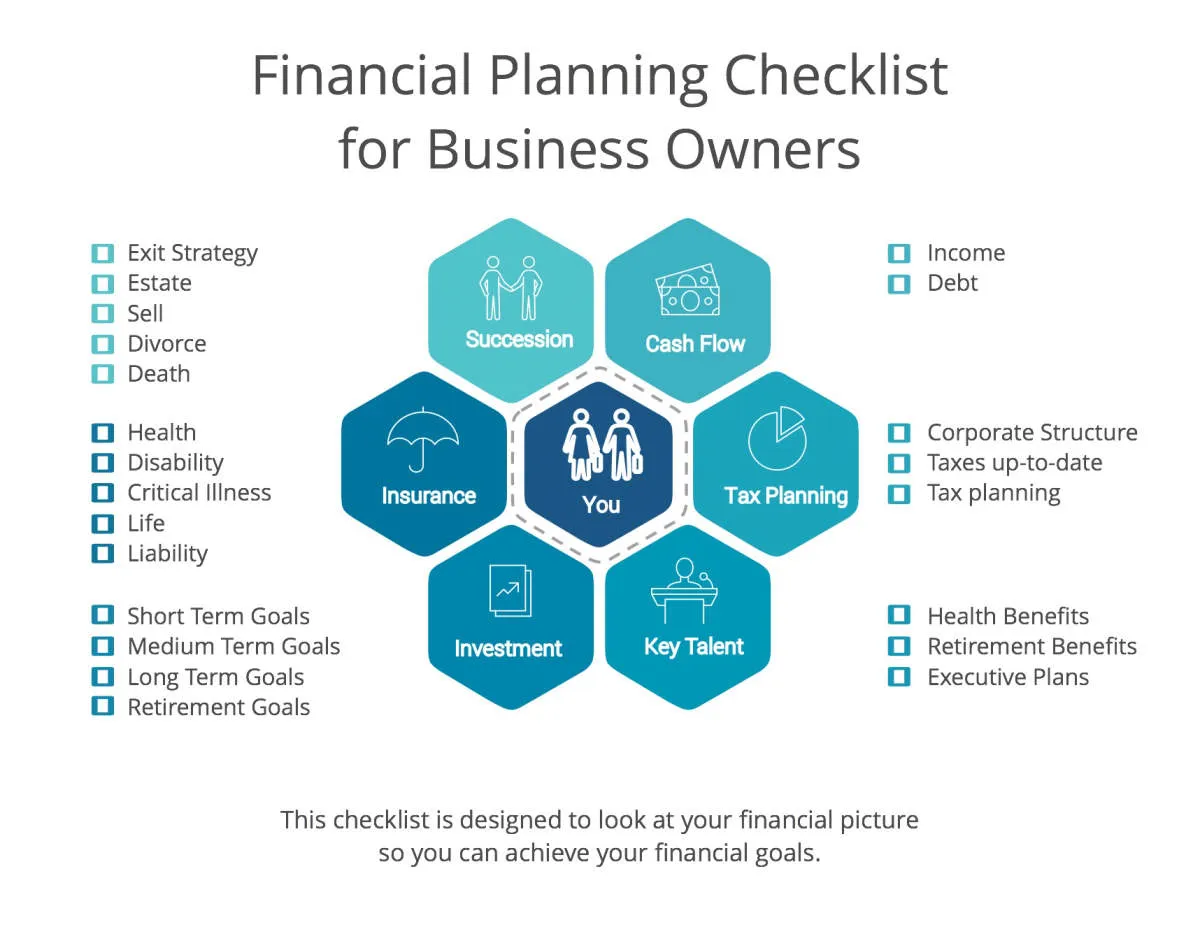
In this article, we will explore essential financial management tips tailored for small business owners to help navigate the complexities of managing finances effectively.
Creating a Financial Plan

A comprehensive financial plan is the backbone of any successful small business. It acts as a roadmap, guiding your financial decisions and helping you reach your business goals. Here’s what to consider when creating your plan:
1. Define Your Financial Goals
Start by clearly outlining your short-term and long-term financial objectives. Do you aim to expand your operations, invest in new equipment, or increase profitability? Having specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals will give you direction and help you track progress.
2. Understand Your Current Financial Situation
You can’t plan for the future without a clear understanding of your present financial standing. This involves:
- Creating a balance sheet: This provides a snapshot of your assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time.
- Developing an income statement: This summarizes your revenues and expenses over a period, revealing your net profit or loss.
- Analyzing your cash flow: Understand the movement of cash in and out of your business to ensure you can meet short-term obligations.
3. Develop a Budgeting Strategy
A well-structured budget is crucial for managing your finances effectively. It involves forecasting your income and expenses, allowing you to:
- Allocate funds appropriately.
- Identify areas for cost savings.
- Track your actual performance against projections.
4. Secure Adequate Funding
Determine if you require external funding to support your business goals. This could involve:
- Seeking small business loans: Explore options from banks or alternative lenders.
- Attracting investors: Prepare a compelling business plan to present to potential investors.
- Bootstrapping: Utilizing your own savings or generating revenue to fund growth.
5. Regularly Review and Adjust
Your financial plan is a living document. As your business evolves, market conditions change, or new opportunities arise, it’s essential to review and adjust your plan accordingly. Regularly monitor your progress, analyze your financial results, and make necessary modifications to stay on track toward your goals.
Managing Cash Flow

Maintaining healthy cash flow is crucial for the survival and growth of any small business. It’s not just about making profits but ensuring you have enough liquid assets to cover your expenses, invest in opportunities, and navigate unexpected challenges.
Here are some key tips for effective cash flow management:
- Accurate Forecasting: Prepare realistic cash flow projections to anticipate future income and expenses. This helps identify potential shortfalls and opportunities for optimizing your financial resources.
- Timely Invoicing and Collections: Invoice promptly and implement efficient collection practices to accelerate incoming payments. Consider offering early payment discounts or using online invoicing platforms.
- Expense Control: Track all expenses diligently and identify areas for potential cost reductions. Negotiate better rates with suppliers, explore cost-effective alternatives, and prioritize essential expenditures.
- Emergency Fund: Establish a cash reserve to cover unexpected expenses or revenue shortfalls. Aim for 3-6 months’ worth of operating expenses to weather unforeseen circumstances.
- Leverage Technology: Utilize accounting software or online tools to simplify financial management tasks, automate processes, and gain real-time insights into your cash flow status.
Reducing Business Expenses

One of the most effective ways to improve your business’s financial health is to reduce expenses. This doesn’t necessarily mean sacrificing quality or cutting corners. Instead, it involves carefully analyzing your spending habits and identifying areas where you can save without negatively impacting your operations.
Here are some practical tips for reducing business expenses:
- Negotiate with Suppliers: Don’t be afraid to negotiate better rates with your suppliers, especially if you’ve been a loyal customer for a while. It’s also worth comparing prices from different suppliers to ensure you’re getting the best deal.
- Embrace Technology: Utilizing technology can lead to significant cost savings. Consider cloud-based software subscriptions over expensive one-time purchases, or explore automation tools to streamline tasks and reduce labor costs.
- Go Paperless: Transitioning to digital documentation, invoices, and communication not only saves on paper and printing costs but also promotes efficiency and reduces storage space requirements.
- Reduce Office Space: If feasible, explore downsizing your office space or adopting a hybrid work model. This can lead to substantial savings on rent, utilities, and other overhead expenses.
- Outsource Strategically: Outsourcing certain business functions, such as accounting, marketing, or customer support, to freelancers or specialized firms can be more cost-effective than hiring full-time employees.
- Review Subscriptions and Memberships: Regularly evaluate all your business subscriptions and memberships. Cancel any that are no longer essential or used frequently enough to justify their cost.
- Cut Utility Costs: Implement energy-saving practices in your workplace, such as using energy-efficient lighting, appliances, and HVAC systems. Encourage employees to conserve energy where possible.
- Monitor and Analyze Expenses: Utilize accounting software or spreadsheets to track your expenses meticulously. Regularly analyze your spending patterns to identify areas for improvement and potential savings.
By implementing these strategies and making conscious decisions about your spending, you can effectively reduce business expenses and improve your overall profitability.
Investing in Your Business

Investing back into your business is crucial for its growth and long-term success. This doesn’t always mean large-scale expansions; it can involve smaller, strategic investments that improve efficiency, reach new customers, or enhance your offerings.
Areas to Consider for Investment:
- Marketing and Advertising: Reaching new customers is vital. Explore online advertising, social media campaigns, or local partnerships.
- Employee Training and Development: A skilled workforce is a productive workforce. Invest in training programs to enhance employee skills and knowledge.
- Technology and Equipment Upgrades: Up-to-date technology and equipment can improve efficiency and productivity. Consider new software, machinery, or tools.
- Product or Service Development: Stay competitive by investing in research and development. Explore new offerings or enhancements to existing ones.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: Building strong customer relationships is key. A CRM system can help manage interactions, track preferences, and improve customer satisfaction.
Tips for Smart Investing:
- Set a Budget: Determine how much you can realistically afford to invest without straining your finances.
- Prioritize: Focus on investments that will yield the highest return on investment (ROI) and align with your business goals.
- Track Results: Monitor the impact of your investments. Are they generating new customers, boosting sales, or improving efficiency?
- Seek Expert Advice: Consult with financial advisors or business mentors to get guidance on investment strategies.
Using Financial Tools

Managing finances effectively is crucial for the success of any small business. Thankfully, there’s a wide array of financial tools available to help you stay organized, make informed decisions, and achieve your financial goals. Here are some essential tools to consider:
1. Accounting Software
Investing in reliable accounting software is non-negotiable. Software like QuickBooks, Xero, or FreshBooks automates tasks such as:
- Tracking income and expenses
- Invoicing clients
- Reconciling bank statements
- Generating financial reports
This saves you time and provides accurate financial data for decision-making.
2. Budgeting and Forecasting Tools
Creating a realistic budget and forecasting future cash flow is essential. Tools like LivePlan, PlanGuru, or even spreadsheet software can assist you in:
- Setting financial goals
- Tracking performance against your budget
- Anticipating potential shortfalls or surpluses
3. Expense Tracking Apps
Keeping tabs on expenses is crucial, especially for small businesses. Mobile apps like Expensify, Zoho Expense, or Wave Receipts simplify the process by allowing you to:
- Scan and digitize receipts
- Categorize expenses
- Generate expense reports for easy accounting integration
4. Inventory Management Software
If your business involves physical products, efficient inventory management is key. Software solutions such as Cin7, DEAR Systems, or TradeGecko help you:
- Track inventory levels in real-time
- Forecast demand and prevent stockouts
- Manage orders and streamline fulfillment
5. Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems
For businesses with direct customer transactions, a POS system is essential. Modern POS systems go beyond processing sales and can:
- Manage customer data
- Track sales trends
- Integrate with inventory and accounting software
Examples include Square, Shopify POS, and Lightspeed.
Reviewing Financial Statements
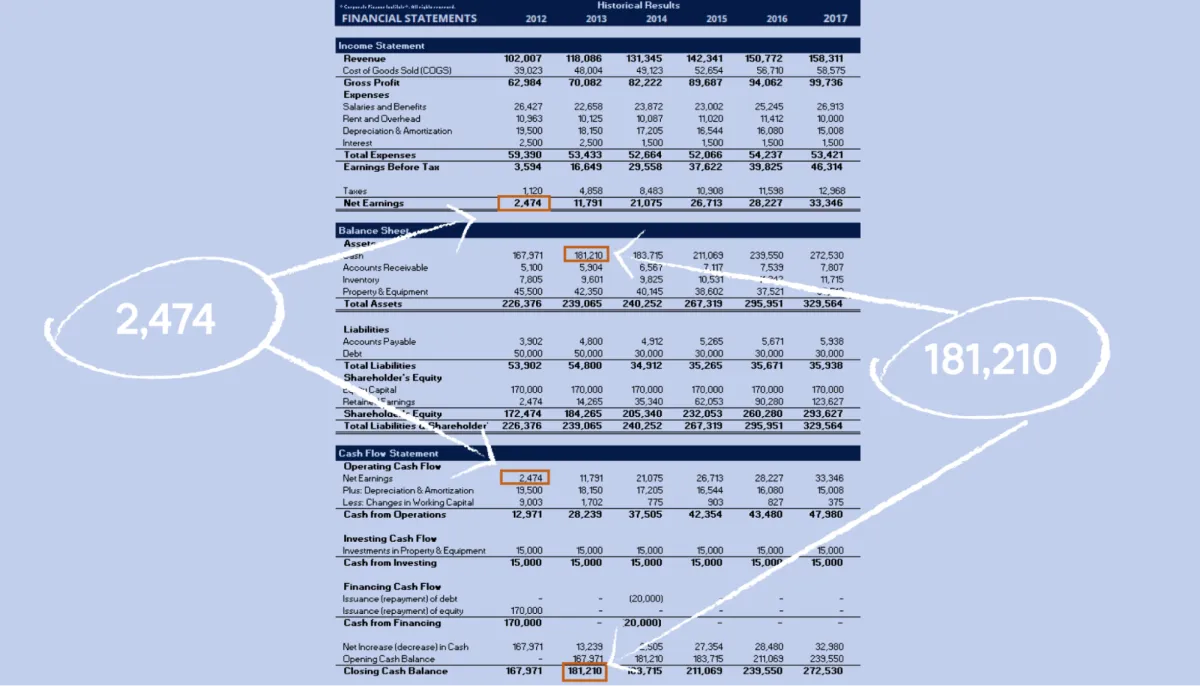
Regularly reviewing your financial statements is crucial for understanding the health of your small business. It allows you to track profitability, identify trends, and make informed decisions. Here’s a breakdown of the key financial statements and what to look for:
1. Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement)
The income statement shows your business’s revenues, expenses, and net profit or loss over a specific period. Key points to review:
- Revenue: Is it growing or declining? Are there any seasonal trends?
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): How much does it cost to produce your product or deliver your service?
- Gross Profit: What’s the difference between your revenue and COGS?
- Operating Expenses: Are your expenses increasing or decreasing? Are there any areas for potential cost savings?
- Net Income: Are you making a profit or loss? What’s the trend over time?
2. Balance Sheet
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of your business’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. Key areas to analyze:
- Assets: What your business owns (e.g., cash, inventory, equipment). Analyze the liquidity of your assets – how easily can they be converted to cash?
- Liabilities: What your business owes to others (e.g., loans, accounts payable). Are you taking on too much debt?
- Equity: The owner’s stake in the business. How much of the business do you actually own?
3. Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement tracks the movement of cash both into and out of your business over a specific period. Analyze:
- Operating Activities: Cash flow from your core business operations.
- Investing Activities: Cash flow from investments in assets like equipment.
- Financing Activities: Cash flow from debt, equity, and dividends.
Understanding your cash flow is vital to ensuring you can meet short-term obligations and plan for future investments.
4. Utilizing Financial Ratios
Financial ratios provide valuable insights into your business’s performance and can be used to compare your results to industry benchmarks. Key ratios to consider:
- Profitability Ratios: Measure your ability to generate profits (e.g., gross profit margin, net profit margin).
- Liquidity Ratios: Assess your ability to meet short-term obligations (e.g., current ratio, quick ratio).
- Solvency Ratios: Measure your long-term financial stability (e.g., debt-to-equity ratio).
Setting Financial Goals
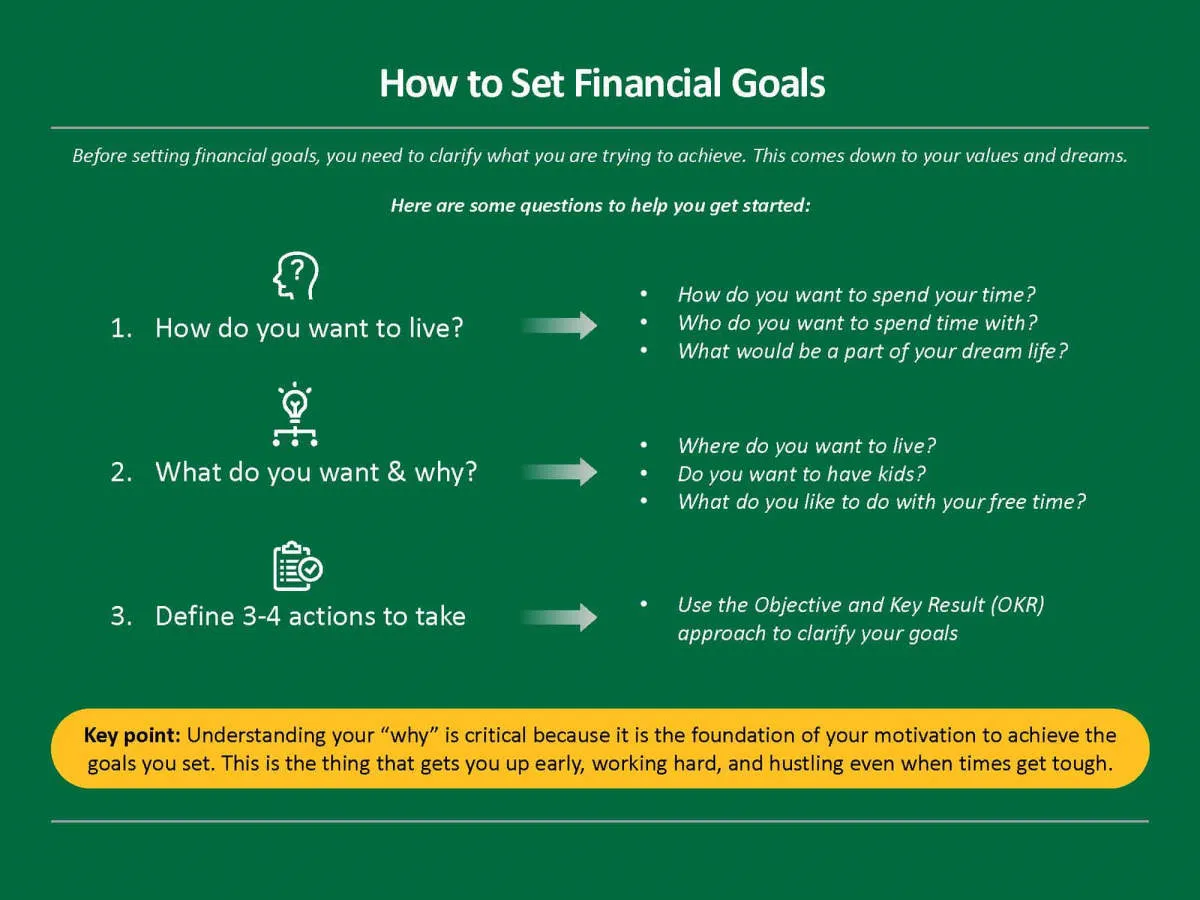
Every small business owner should prioritize setting clear and specific financial goals. These goals serve as a roadmap, guiding financial decisions and ensuring the long-term health and growth of your business.
Here are some key points to consider when setting financial goals:
Types of Financial Goals
- Short-Term Goals: These are goals you aim to achieve within the next year, such as increasing sales revenue by a certain percentage or reducing operating expenses.
- Long-Term Goals: These goals typically span several years or more and focus on broader objectives, like expanding into new markets, acquiring another business, or planning for retirement.
SMART Goals
Ensure your financial goals are SMART:
- Specific: Clearly define what you want to achieve.
- Measurable: Use quantifiable metrics to track progress.
- Achievable: Set realistic goals within your business’s capabilities.
- Relevant: Align your goals with your overall business objectives.
- Time-Bound: Establish deadlines to provide a sense of urgency.
Examples of Financial Goals
- Increase net profit margin by 5% over the next fiscal year.
- Build a cash reserve equivalent to six months of operating expenses within three years.
- Secure a business loan of $50,000 for equipment upgrades within the next 12 months.
- Achieve $1 million in annual revenue within the next five years.
Building an Emergency Fund

Just like individuals, small businesses need a safety net. Unexpected expenses like equipment repairs, economic downturns, or even a sudden legal issue can significantly impact your business’s cash flow. That’s where an emergency fund becomes a lifeline.
Why is it Crucial for Small Businesses?
Having an emergency fund specifically for your business offers several benefits:
- Business Continuity: Cover operational expenses and avoid debt even during lean times.
- Crisis Management: Respond swiftly to unexpected challenges without derailing your business plan.
- Opportunity Grabbing: Seize time-sensitive business opportunities that require immediate capital.
- Peace of Mind: Focus on growth and strategic decisions with reduced financial stress.
How to Build Your Emergency Fund:
Building a robust emergency fund takes time and discipline. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Set a Realistic Goal: Aim for 3-6 months’ worth of essential business expenses. This may include rent, utilities, payroll, inventory, and loan repayments.
- Automate Savings: Treat your emergency fund contributions like any other business expense. Schedule regular automatic transfers to a separate savings account.
- Start Small, Stay Consistent: Even small, regular contributions add up over time. Begin with an achievable amount and gradually increase it as your business grows.
- Windfalls and Surplus: Deposit any unexpected income, such as tax refunds or a particularly profitable month, directly into your emergency fund.
- Review and Adjust: Periodically reassess your emergency fund goals. As your business expenses grow, so should your savings target.
Seeking Professional Advice

While there are many resources available to help you manage your business finances yourself, sometimes seeking professional advice is invaluable. Financial experts can provide tailored guidance and support to optimize your financial strategies.
When to Consider Professional Advice:
- Complex financial situations: If your business involves intricate transactions, multiple revenue streams, or significant investments, a financial advisor can help you navigate complexities and minimize risks.
- Tax planning and compliance: Tax laws can be complex and ever-changing. A qualified accountant or tax professional can ensure you meet all legal requirements and optimize your tax strategies.
- Business expansion or financing: Seeking external funding or expanding your operations often requires a solid financial plan and understanding of funding options. Financial advisors can guide you through the process and help you secure the best terms.
- Feeling overwhelmed: Managing business finances can be time-consuming and demanding. If you feel overwhelmed or lack confidence in certain areas, seeking professional help can free up your time and provide peace of mind.
Types of Financial Professionals:
- Accountants: Manage day-to-day bookkeeping, prepare financial statements, and provide tax advice.
- Financial advisors: Offer comprehensive financial planning, including budgeting, investing, and retirement planning.
- Business consultants: Specialize in improving business operations, including financial management strategies.
When choosing a financial professional, consider their experience, qualifications, and areas of expertise. Look for professionals with a strong understanding of small businesses and your specific industry. It’s essential to establish a trusting relationship with your advisor, ensuring clear communication and aligned financial goals.
Understanding Business Taxes

Navigating the world of business taxes can feel complex, but it’s crucial for small business owners to grasp the fundamentals. Here’s a breakdown to help you understand your tax obligations:
1. Business Structure and Taxes:
Your business structure (sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, corporation) dictates how you’ll file and pay taxes. For example:
- Sole proprietorships report income and expenses on their personal tax returns (Form 1040).
- Corporations file separate corporate tax returns.
2. Common Types of Business Taxes:
Familiarize yourself with the types of taxes your business might be subject to. These often include:
- Income Tax: Levied on your business profits.
- Self-Employment Tax: If you’re self-employed, you’ll pay this to cover Social Security and Medicare.
- Sales Tax: Collected on goods or services you sell (rates vary by state and locality).
- Payroll Tax: Applies if you have employees, covering taxes for Social Security, Medicare, and unemployment.
3. Estimated Taxes:
Instead of paying taxes annually, businesses are often required to make estimated tax payments throughout the year. The frequency (quarterly, monthly) depends on factors like your income level.
4. Record Keeping:
Accurate and organized financial records are essential for tax purposes. Keep track of all income and expenses, categorize them appropriately, and retain receipts and invoices.
5. Seeking Professional Guidance:
Tax laws can be intricate. Consider consulting with a qualified tax professional or accountant, especially when starting your business or facing significant financial decisions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, implementing smart financial management practices is crucial for small business owners to ensure long-term success and sustainability.