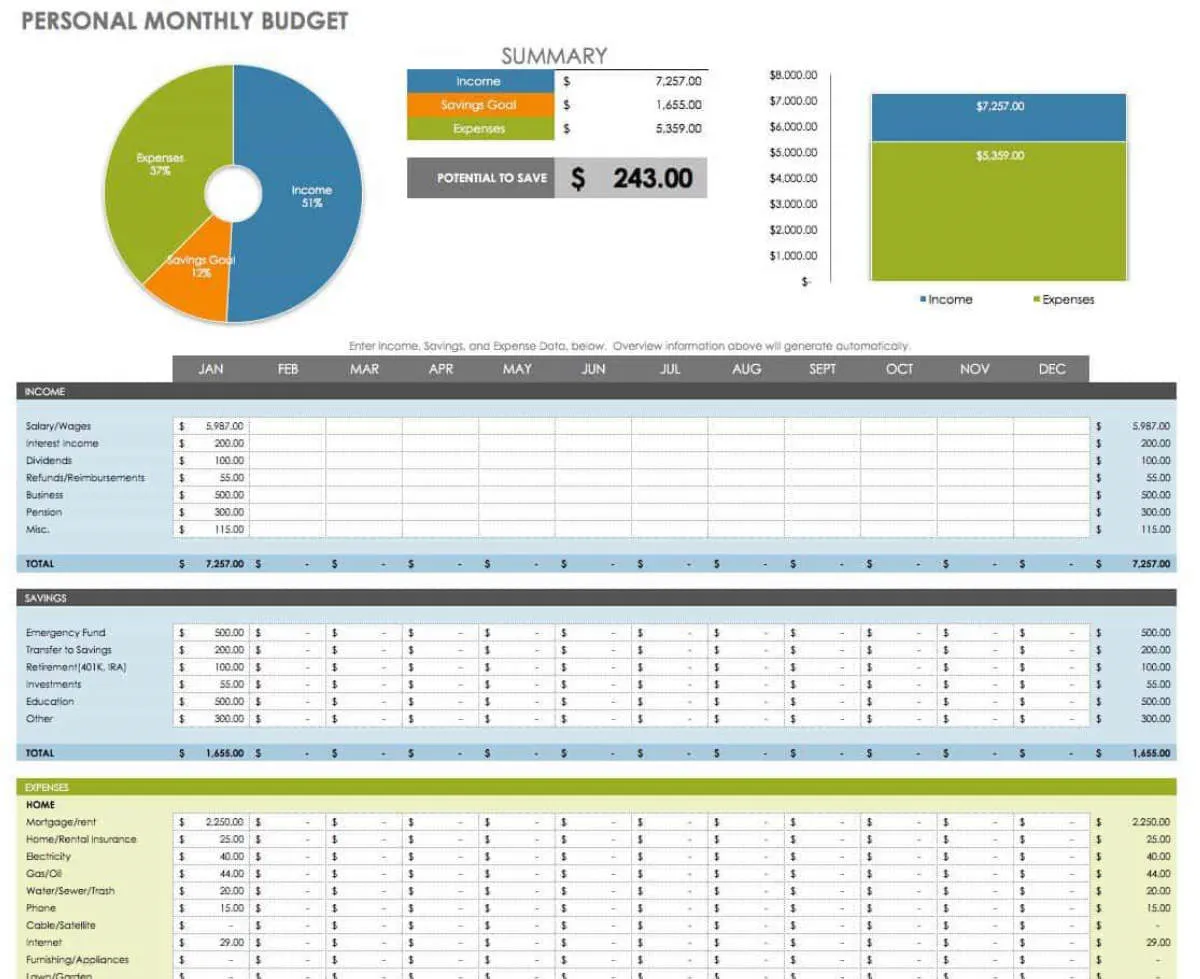
In this article, discover expert tips on how to create a solid personal financial plan that can help you achieve your financial goals and secure your future financial stability.
Understanding Financial Planning

Financial planning is the cornerstone of achieving your financial goals, whether it’s buying a home, retiring comfortably, or securing your family’s future. It provides a roadmap to navigate your finances effectively and make informed decisions about your money.
Here’s what financial planning encompasses:
1. Assessing Your Current Financial Situation
Before creating a plan, you need a clear picture of where you stand financially. This includes:
- Income and Expenses: Track your income sources and all your expenses to understand your cash flow.
- Assets and Liabilities: List down everything you own (assets) and owe (liabilities), like loans or credit card debt.
- Net Worth: Calculate your net worth by subtracting your liabilities from your assets. This gives you a snapshot of your overall financial health.
2. Setting SMART Financial Goals
Identify your short-term and long-term financial aspirations. Ensure your goals are:
- Specific
- Measurable
- Attainable
- Relevant
- Time-bound
For example, instead of “saving more money,” a SMART goal could be “saving $5,000 for a down payment on a car within two years.”
3. Creating a Budget and Sticking to It
A budget is crucial for tracking your income and expenses and ensuring you’re allocating funds towards your goals. It helps you control spending, save effectively, and avoid debt.
4. Managing Debt Effectively
High-interest debts can derail your financial progress. Prioritize paying down high-interest debts first and explore strategies like debt consolidation to manage your liabilities effectively.
5. Investing for the Future
Investing is essential for growing your wealth over time. Determine your risk tolerance, explore different investment options like stocks, bonds, or real estate, and consider diversifying your portfolio.
6. Protecting Yourself and Your Assets
Insurance plays a vital role in safeguarding yourself and your loved ones from financial risks. This includes health insurance, life insurance, disability insurance, and property insurance.
7. Planning for Retirement
Start planning for retirement early on to ensure a comfortable life after you stop working. Explore retirement savings plans, estimate your retirement expenses, and consider factors like inflation.
8. Reviewing and Adjusting Your Plan Regularly
Your financial situation and goals may change over time. It’s crucial to review and adjust your financial plan periodically to stay on track and ensure it aligns with your evolving needs.
Setting Financial Goals
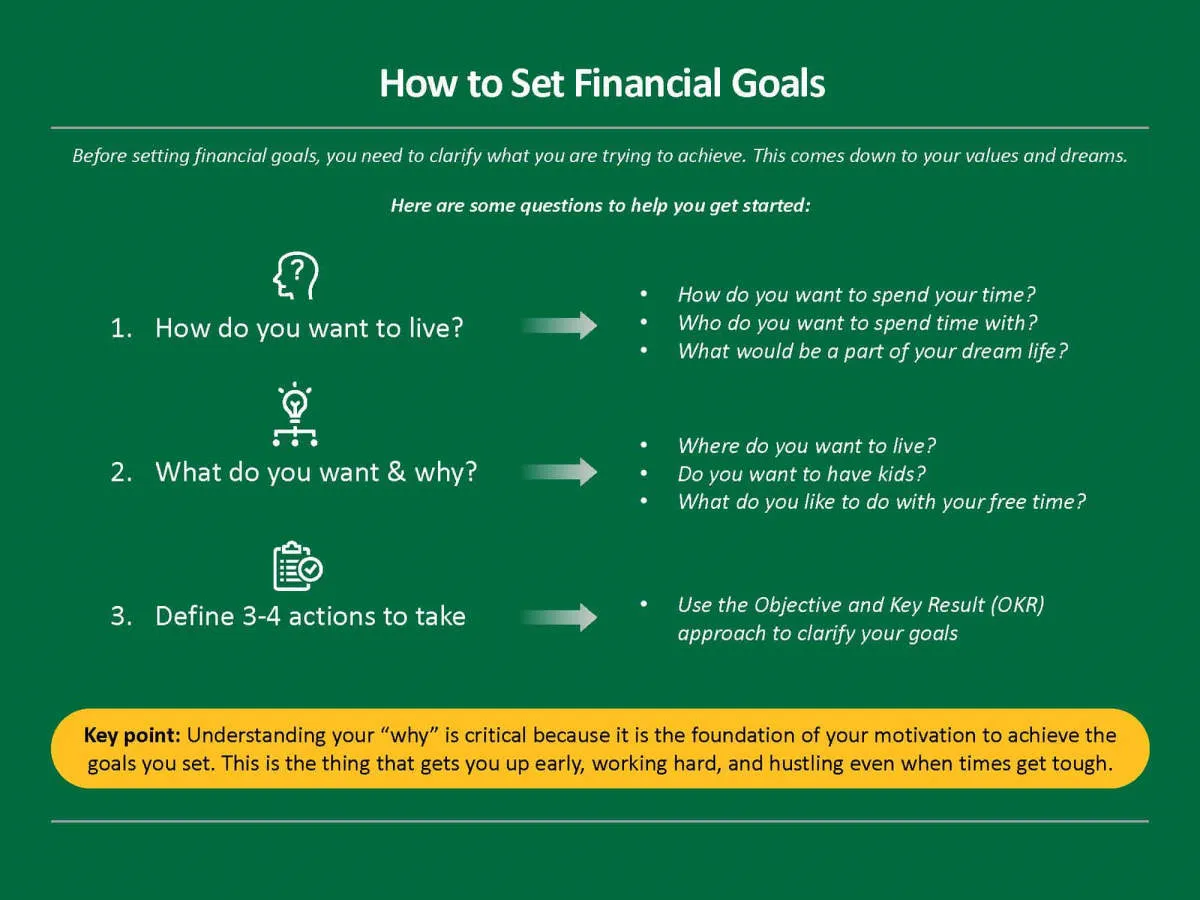
Setting clear and specific financial goals is the crucial first step in crafting your personal financial plan. These goals act as your roadmap, guiding your saving and spending habits and helping you achieve the financial future you desire.
Types of Financial Goals:
Financial goals can span different timeframes and purposes. It’s helpful to categorize them as:
- Short-term goals (achievable within 1 year): Examples include building an emergency fund, paying off a credit card, or saving for a vacation.
- Mid-term goals (achievable in 1-5 years): These could involve saving for a down payment on a house, buying a car, or paying off a significant portion of student loans.
- Long-term goals (5+ years): Typical long-term goals are planning for retirement, saving for a child’s education, or investing in real estate.
Making Your Goals SMART:
To set yourself up for success, ensure your financial goals follow the SMART criteria:
- Specific: Clearly define what you want to achieve (e.g., “Save $10,000 for a down payment”).
- Measurable: Quantify your goal with a specific amount (e.g., save $500 per month).
- Achievable: Be realistic about your income and expenses, setting goals you can reasonably meet.
- Relevant: Choose goals that align with your values and priorities.
- Time-bound: Set a deadline for achieving your goal to stay motivated.
Prioritizing Your Goals:
It’s common to have multiple financial goals. Prioritize them based on urgency and importance. For example, building an emergency fund might take precedence over saving for a vacation.
Creating a Budget

A budget is a plan for how you will spend your money each month. It helps you track your income and expenses, so you can make sure you’re not spending more than you earn. Creating a budget can seem daunting, but it’s easier than you might think. Here’s a step-by-step guide to get you started:
1. Track Your Income and Expenses
The first step to creating a budget is to understand your cash flow. Track all sources of income, including your salary, wages, bonuses, investment returns, and any other regular income streams.
Next, track your expenses. Monitor all your spending habits for a month, noting every dollar spent. This includes fixed expenses like rent/mortgage, utilities, and loan payments, as well as variable expenses like groceries, entertainment, and dining out.
2. Categorize Your Spending
Once you have a clear picture of your income and expenses, categorize your spending. Common categories include housing, transportation, food, utilities, healthcare, entertainment, debt repayment, and savings.
3. Set Financial Goals
What do you want to achieve with your money? Identifying your financial goals will help you prioritize your spending and stay motivated to stick to your budget. Common financial goals include saving for retirement, buying a home, paying off debt, or investing for the future.
4. Create Your Budget
Now it’s time to build your budget. Allocate your income towards different expense categories, ensuring that your expenses don’t exceed your income. There are various budgeting methods available, such as the 50/30/20 budget, the envelope system, or zero-based budgeting. Choose a method that aligns with your financial goals and preferences.
5. Automate Your Savings
Treat your savings as a non-negotiable expense. Set up automatic transfers from your checking account to your savings account each month. This will help you build a healthy savings habit and reach your financial goals faster.
6. Review and Adjust
Your financial situation and goals may change over time, so it’s essential to regularly review and adjust your budget. Aim to review your budget at least monthly, or more frequently if your circumstances change significantly. This will help you stay on track and make necessary adjustments along the way.
Building an Emergency Fund

One of the cornerstones of a solid financial plan is a well-stocked emergency fund. This fund acts as a financial safety net, protecting you from the unexpected bumps in life’s road. Without one, you might find yourself relying on high-interest credit cards or loans when faced with unexpected expenses, potentially derailing your financial goals.
So, how much should you save? A good rule of thumb is to aim for 3-6 months’ worth of essential living expenses. These expenses include:
- Rent or mortgage payments
- Utilities
- Groceries
- Transportation costs
- Debt payments
- Insurance premiums
Where to Keep Your Emergency Fund
Accessibility and safety are key when choosing where to keep your emergency fund. Consider these options:
- High-yield savings accounts: These accounts offer higher interest rates than traditional savings accounts, helping your money grow faster.
- Money market accounts: Similar to savings accounts, these often come with check-writing privileges and may offer slightly higher interest rates.
Tips for Building Your Emergency Fund
- Start small: Even setting aside a small amount each week adds up over time.
- Automate your savings: Set up automatic transfers from your checking account to your emergency fund.
- Make it a priority: Treat your emergency fund contributions like any other essential bill.
- Replenish when needed: If you need to dip into your emergency fund, make sure to replenish it as soon as possible.
Investing for the Future

Investing is a crucial aspect of securing your financial future. It allows you to grow your money over time and potentially outpace inflation. By investing wisely, you can build wealth, achieve your financial goals, and create a more secure future for yourself and your loved ones.
Why Invest?
Investing offers several key benefits, including:
- Wealth Accumulation: Investing allows your money to work for you, potentially earning higher returns than traditional savings accounts.
- Inflation Hedge: Investments can help your money keep pace with or even outpace inflation, preserving its purchasing power over time.
- Financial Goals: Investing can help you reach your long-term financial goals, such as buying a home, funding your children’s education, or retiring comfortably.
- Compound Growth: Over time, even small investments can grow significantly through the power of compound interest, where your earnings generate even more earnings.
Getting Started with Investing
To begin investing, consider the following steps:
- Set Clear Goals: Determine your investment objectives, such as the amount of money you want to accumulate, the timeframe for your investments, and your risk tolerance.
- Create a Budget: Track your income and expenses to identify areas where you can save and invest regularly.
- Build an Emergency Fund: Before investing, establish an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses and avoid dipping into your investments prematurely.
- Choose Investments: Explore different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and real estate, and select investments that align with your risk tolerance and financial goals.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Spreading your investments across multiple asset classes can help mitigate risk and enhance potential returns.
- Start Small and Be Consistent: Begin with manageable investment amounts and contribute regularly to your portfolio.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consider consulting with a qualified financial advisor to receive personalized guidance and optimize your investment strategy.
Managing Debt

Debt is a fact of life for many people, but it’s important to manage it carefully so it doesn’t derail your financial goals. Here are some tips for getting a handle on your debt:
1. Know What You Owe
The first step to managing debt is understanding exactly how much you owe. Make a list of all your debts, including credit cards, student loans, auto loans, and any other outstanding balances. Note the interest rate, minimum payment, and total amount owed for each debt.
2. Create a Debt Repayment Plan
Once you have a clear picture of your debt, create a plan for paying it down strategically. There are two popular methods:
- The Debt Snowball: Focus on paying off the smallest debt first, regardless of interest rate. This can provide motivation as you see quick wins.
- The Debt Avalanche: Prioritize debts with the highest interest rates, saving you money on interest payments over time.
Choose the method that best suits your personality and financial situation.
3. Negotiate Lower Interest Rates
Don’t be afraid to contact your creditors and negotiate lower interest rates. Explain your financial situation and commitment to repayment. A lower interest rate can save you a significant amount of money over the life of the loan.
4. Explore Debt Consolidation or Refinancing Options
If you have multiple high-interest debts, consider consolidating them into a single loan with a lower interest rate. Refinancing existing loans, such as student loans or mortgages, can also help reduce your monthly payments or overall interest paid.
5. Avoid Taking on New Debt
As you work towards paying off existing debt, make a conscious effort to avoid taking on new debt. This may require adjustments to your spending habits and finding ways to live within your means.
6. Seek Professional Help If Needed
If you’re struggling to manage your debt or feel overwhelmed, don’t hesitate to seek help from a certified financial advisor. They can provide personalized guidance and support to help you achieve your financial goals.
Using Financial Tools

Creating a personal financial plan can feel overwhelming, but utilizing available financial tools can simplify the process and provide valuable insights. These tools range from budgeting apps and online calculators to professional financial planning software. Here’s how they can help:
1. Budgeting and Expense Tracking:
Numerous apps and software programs automate budgeting and expense tracking. They can link to your bank accounts and credit cards, categorizing transactions and providing a clear picture of your spending habits. This visual representation helps identify areas for potential savings and allows for better allocation of funds.
2. Debt Management Tools:
If you have debt, several tools can assist in managing and reducing it. Debt snowball calculators, for example, help prioritize debt payments, while loan amortization schedules visualize the impact of making extra payments. Some apps even offer debt consolidation options.
3. Investment Platforms and Robo-Advisors:
Investing can seem daunting, but online platforms and robo-advisors have made it more accessible. These platforms often require low minimum investments and offer diversified portfolio options based on your risk tolerance and investment goals. They automate the investment process, rebalancing your portfolio as needed.
4. Retirement Planning Calculators:
Planning for retirement is crucial. Online retirement calculators can estimate how much you need to save based on your desired retirement age, income goals, and estimated life expectancy. They can also help determine the effectiveness of different savings and investment strategies.
5. Financial Planning Software:
For a more comprehensive approach, consider financial planning software. These programs typically offer a suite of tools encompassing budgeting, debt management, investment tracking, retirement planning, and more. They provide a holistic view of your financial situation and allow for more sophisticated analysis and forecasting.
Remember: While financial tools can be incredibly beneficial, it’s essential to choose tools that align with your specific needs and goals. Research different options, read reviews, and don’t hesitate to seek guidance from a qualified financial advisor if needed.
Reviewing and Adjusting Your Plan

Creating a personal financial plan isn’t a “set it and forget it” kind of task. Life is constantly changing, and your financial plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to those changes. That’s why regular review and adjustment are crucial.
When to Review
Aim to review your financial plan at least once a year. However, certain life events might require a more frequent review. These events could include:
- Significant changes in income (increase or decrease)
- Job loss or a career change
- Marriage or divorce
- Birth or adoption of a child
- Unexpected expenses (medical bills, major home repairs)
- Receiving an inheritance or a large sum of money
What to Review
During your review, take a comprehensive look at the following aspects of your plan:
- Budget: Are your income and expenses still accurate? Do you need to adjust your spending habits in any areas?
- Debt Management: Are you on track with your debt repayment goals? Have any new debts emerged that need to be addressed?
- Emergency Fund: Is your emergency fund still sufficient to cover 3-6 months of living expenses?
- Investments: Are your investments aligned with your risk tolerance and financial goals? Do you need to rebalance your portfolio?
- Insurance Coverage: Do you have adequate insurance coverage (health, life, disability, property) for your current situation?
- Retirement Savings: Are you saving enough for retirement? Do you need to adjust your contribution levels based on your current income and expenses?
Making Adjustments
Based on your review, don’t hesitate to make necessary adjustments to your plan. These adjustments could involve:
- Modifying your budget and spending habits
- Exploring debt consolidation or refinancing options
- Adjusting your investment strategy
- Updating your insurance coverage
- Increasing your retirement contributions
Building Good Financial Habits

Creating a personal financial plan is only the first step. The true magic happens when you cultivate healthy financial habits that support your plan and set you up for long-term success. Here’s how:
1. Track Your Spending:
You can’t manage what you don’t measure. Utilize budgeting apps, spreadsheets, or even a simple notebook to monitor where your money goes. This awareness is crucial for identifying areas where you can cut back and save more effectively.
2. Automate Your Savings:
Make saving a no-brainer by setting up automatic transfers from your checking account to your savings or investment accounts. This ensures you consistently contribute to your financial goals, even before you have a chance to spend the money.
3. Live Below Your Means:
Resist the allure of lifestyle inflation. Just because you get a raise doesn’t mean you need to upgrade your lifestyle instantly. Prioritize saving and investing any extra income you receive.
4. Set Realistic Financial Goals:
Break down your long-term financial aspirations into smaller, achievable milestones. This makes the overall journey less daunting and allows you to celebrate small victories along the way, keeping you motivated.
5. Review and Adjust Regularly:
Financial situations are dynamic, so your plan shouldn’t be static. Regularly review your budget, track your progress towards your goals, and make necessary adjustments to stay on track with your evolving needs and circumstances.
6. Seek Financial Literacy:
Continuously educate yourself about personal finance. Read books, listen to podcasts, or take courses to enhance your financial knowledge and make well-informed decisions about your money. This empowers you to navigate complex financial products and strategies with confidence.
Seeking Professional Advice

While creating a personal financial plan on your own is admirable, seeking advice from a financial advisor can provide invaluable expertise and personalized guidance. Financial advisors can help you:
- Assess your current financial situation: They can analyze your income, expenses, assets, and debts to get a clear picture of your financial health.
- Define specific financial goals: Whether it’s buying a home, saving for retirement, or funding your children’s education, an advisor can help you set realistic and achievable goals.
- Develop a tailored financial plan: Based on your goals and risk tolerance, they can create a customized plan that outlines investment strategies, savings plans, and debt management techniques.
- Navigate complex financial products: From investment options to insurance policies, financial advisors can explain complex financial products in simple terms and recommend suitable choices.
- Provide ongoing support and adjustments: As your life circumstances change, an advisor can help you adjust your financial plan accordingly and ensure you stay on track to reach your goals.
When choosing a financial advisor, consider their credentials, experience, and fee structure. Look for a Certified Financial Planner (CFP) or a Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) who has a fiduciary duty to act in your best interest.
Conclusion
In conclusion, creating a personal financial plan is crucial for a stable future. Set clear goals, budget wisely, save consistently, and invest smartly to achieve financial freedom.